Agrobacterium-Mediated Transformation of the Dwarf Soybean MiniMax
- PMID: 38611542
- PMCID: PMC11013704
- DOI: 10.3390/plants13071013
Agrobacterium-Mediated Transformation of the Dwarf Soybean MiniMax
Abstract
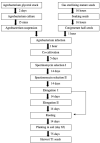
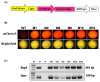
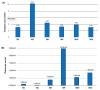
This study aims to establish an Agrobacterium-mediated transformation system for use with the 'MiniMax'soybean cultivar. MiniMax is a mutant soybean whose growth cycle is around 90 days, half that of most other soybean varieties, making it an optimal model cultivar to test genes of interest before investing in modification of elite lines. We describe an efficient protocol for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation using MiniMax seeds. It uses a modified 'half seed' regeneration protocol for transgenic soybean production, utilizing the rapid generation MiniMax variety to obtain T1 seeds in approximately 145 days. Addition of phloroglucinol (PG) to the regeneration protocol was key to obtaining high-efficiency rooting of the regenerated shoots. Transfer to soil was accomplished using an organic soil amendment containing nutrients and mycorrhiza for plants to thrive in the greenhouse. This combination of genotype and stimulants provides a transformation protocol to genetically engineer MiniMax seeds with a transgenic lab-to-greenhouse production efficiency of 4.0%. This is the first report of MiniMax soybean whole plant transformation and heritable T1 transmission. This protocol provides an ideal resource for enhancing the genetic transformation of any soybean cultivar.
Keywords: MiniMax cultivar; mycorrhiza fungi; phloroglucinol; regeneration; soybean; transformation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Matthews B.F., MacDonald M.H., Song Q.J., Cregan P.B., Lewers K.S. Registration of ‘MiniMax’ Soybean. J. Plant Regist. 2007;1:97–98. doi: 10.3198/jpr2006.10.0653crc. - DOI
-
- Klink V.P., MacDonald M.H., Martins V.E., Park S.-C., Kim K.-H., Baek S.-H., Matthews B.F. MiniMax, a new diminutive Glycine max genotype with a rapid life cycle, embryogenic potential and transformation capabilities. Plant Cell Tissue Organ. Cult. 2008;92:183–195. doi: 10.1007/s11240-007-9323-3. - DOI
-
- Kocsy G., Simon-Sarkadi L., Galiba G., de Ronde J.A. Transformation of Soybean and Transgenic Lines in Basic and Applied Research. Transgenic Plant J. 2007;1:129–144.
-
- Loganathan L., Maruthasalam S., Shiu L.Y., Lien W.C., Hsu W.H., Lee P.F., Yu C.W., Lin C.H. Regeneration of soybean (Glycine max, L. Merrill) through direct somatic embryogenesis from the immature embryonic shoot tip. Vitr. Cell Dev. Biol. Plant. 2010;46:265–273. doi: 10.1007/s11627-009-9263-1. - DOI
-
- Paes de Melo B., Lourenço-Tessutti I.T., Morgante C.V., Santos N.C., Pinheiro L.B., de Jesus Lins C.B., Silva M.C.M., Macedo L.L.P. Fontes EPB and Grossi-de-Sa MF Soybean Embryonic Axis Transformation: Combining Biolistic and Agrobacterium-Mediated Protocols to Overcome Typical Complications of In Vitro Plant Regeneration. Front. Plant Sci. 2020;11:1228. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.01228. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

