Synthetic Routes and Clinical Application of Representative Small-Molecule EGFR Inhibitors for Cancer Therapy
- PMID: 38611728
- PMCID: PMC11012680
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29071448
Synthetic Routes and Clinical Application of Representative Small-Molecule EGFR Inhibitors for Cancer Therapy
Abstract
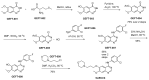
The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) plays a pivotal role in cancer therapeutics, with small-molecule EGFR inhibitors emerging as significant agents in combating this disease. This review explores the synthesis and clinical utilization of EGFR inhibitors, starting with the indispensable role of EGFR in oncogenesis and emphasizing the intricate molecular aspects of the EGFR-signaling pathway. It subsequently provides information on the structural characteristics of representative small-molecule EGFR inhibitors in the clinic. The synthetic methods and associated challenges pertaining to these compounds are thoroughly examined, along with innovative strategies to overcome these obstacles. Furthermore, the review discusses the clinical applications of FDA-approved EGFR inhibitors such as erlotinib, gefitinib, afatinib, and osimertinib across various cancer types and their corresponding clinical outcomes. Additionally, it addresses the emergence of resistance mechanisms and potential counterstrategies. Taken together, this review aims to provide valuable insights for researchers, clinicians, and pharmaceutical scientists interested in comprehending the current landscape of small-molecule EGFR inhibitors.
Keywords: EGFR; application; small molecule; synthetic routes; tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no financial interests.
Figures
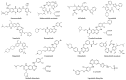





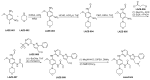


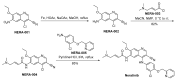


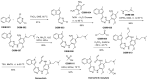






References
-
- Yun C.H., Boggon T.J., Li Y., Woo M.S., Greulich H., Meyerson M., Eck M.J. Structures of lung cancer-derived EGFR mutants and inhibitor complexes: Mechanism of activation and insights into differential inhibitor sensitivity. Cancer Cell. 2007;11:217–227. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2006.12.017. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wood E.R., Truesdale A.T., McDonald O.B., Yuan D., Hassell A., Dickerson S.H., Ellis B., Pennisi C., Horne E., Lackey K., et al. A unique structure for epidermal growth factor receptor bound to GW572016 (Lapatinib): Relationships among protein conformation, inhibitor off-rate, and receptor activity in tumor cells. Cancer Res. 2004;64:6652–6659. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-1168. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Moyer J.D., Barbacci E.G., Iwata K.K., Arnold L., Boman B., Cunningham A., DiOrio C., Doty J., Morin M.J., Moyer M.P., et al. Induction of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest by CP-358,774, an inhibitor of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase. Cancer Res. 1997;57:4838–4848. - PubMed
-
- Li D., Ambrogio L., Shimamura T., Kubo S., Takahashi M., Chirieac L.R., Padera R.F., Shapiro G.I., Baum A., Himmelsbach F., et al. BIBW2992, an irreversible EGFR/HER2 inhibitor highly effective in preclinical lung cancer models. Oncogene. 2008;27:4702–4711. doi: 10.1038/onc.2008.109. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

