Influence of Layer Thickness and Shade on the Transmission of Light through Contemporary Resin Composites
- PMID: 38612069
- PMCID: PMC11012366
- DOI: 10.3390/ma17071554
Influence of Layer Thickness and Shade on the Transmission of Light through Contemporary Resin Composites
Abstract
Background: Material-dependent parameters have an important impact on the efficiency of light polymerization. The present in vitro study aimed to investigate the influence of the increment thickness and shade of nano- and nanohybrid resin composites on the transmission of curing light.
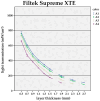
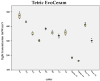
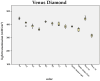
Methods: Three contemporary resin composites were evaluated: Tetric EvoCeram® (TEC); Venus Diamond® (VD); and Filtek Supreme XTE® (FS XTE). Light transmission (LT) was recorded in accordance with the sample thickness (0.5 to 2.7 mm) and the shade. Polymerized samples were irradiated for 10 s each using the high-power LED curing light Celalux 2 (1900 mW/cm2). LT was simultaneously recorded using the MARC Patient Simulator (MARC-PS).
Results: LT was strongly influenced by the composite layer thickness. For 0.5 mm-thick samples, a mean power density of 735 mW/cm2 was recorded at the bottom side. For the 2.7 mm samples, a mean power density of 107 mW/cm2 was measured. Only LT was markedly reduced in the case of darker shades. From A1 to A4, LT decreased by 39.3% for FS XTE and 50.8% for TEC. Dentin shades of FS XTE and TEC (A2, A4) showed the lowest LT.
Conclusions: The thickness and shade of resin composite increments strongly influences the transmission of curing light. More precise information about these parameters should be included in the manufacture manual.
Keywords: MARC PS; layer thickness; light transmission; nanocomposite; photopolymerization; shade.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Determination of polymerization shrinkage of different composites using a photoelastic method.Am J Dent. 2017 Feb;30(1):16-22. Am J Dent. 2017. PMID: 29178709
-
Evaluation of degree of conversion, rate of cure, microhardness, depth of cure, and contraction stress of new nanohybrid composites containing pre-polymerized spherical filler.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2020 Nov 28;31(12):127. doi: 10.1007/s10856-020-06464-9. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2020. PMID: 33247779
-
Influence of increment thickness on microhardness and dentin bond strength of bulk fill resin composites.Dent Mater. 2014 Oct;30(10):1104-12. doi: 10.1016/j.dental.2014.07.001. Epub 2014 Jul 30. Dent Mater. 2014. PMID: 25086481
-
Effect of shade, opacity and layer thickness on light transmission through a nano-hybrid dental composite during curing.J Esthet Restor Dent. 2017 Sep;29(5):362-367. doi: 10.1111/jerd.12311. Epub 2017 Jun 19. J Esthet Restor Dent. 2017. PMID: 28628735
-
Light energy transmission through composite influenced by material shades.Bull Tokyo Dent Coll. 2009;50(4):183-90. doi: 10.2209/tdcpublication.50.183. Bull Tokyo Dent Coll. 2009. PMID: 20179393
Cited by
-
Suitability of Direct Resin Composites in Restoring Endodontically Treated Teeth (ETT).Materials (Basel). 2024 Jul 26;17(15):3707. doi: 10.3390/ma17153707. Materials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39124371 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

