Clays and Wound Healing
- PMID: 38612205
- PMCID: PMC11012786
- DOI: 10.3390/ma17071691
Clays and Wound Healing
Abstract
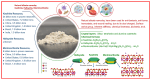
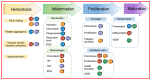
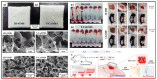
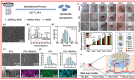
Aluminosilicates, such as montmorillonite, kaolinite, halloysite, and diatomite, have a uniform bidimensional structure, a high surface-to-volume ratio, inherent stiffness, a dual charge distribution, chemical inertness, biocompatibility, abundant active groups on the surface, such as silanol (Si-OH) and/or aluminol (Al-OH) groups. These compounds are on the list of U.S. Food and Drug Administration-approved active compounds and excipients and are used for various medicinal products, such as wound healing agents, antidiarrheals, and cosmetics. This review summarizes the wound healing mechanisms related to the material characteristics and the chemical components. Numerous wound dressings with different active components and multiple forms have been studied. Then, medicinal mineral resources for use in hemostatic materials can be developed.
Keywords: aluminosilicate; clay; hemostasis mechanism; hemostatic material; ionic effect.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funder was not involved in the study design, collection, analysis, interpretation of data, the writing of this article or the decision to submit it for publication.
Figures







References
-
- Tian G., Zhang Y., Jiang Y., Hu P., Wang H., Zhang Y. Nanoscale Zerovalent Iron-Incorporated Kaolinite for Hemostatic and Antibacterial Applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023;636:157879. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2023.157879. - DOI
-
- Teng L., Shao Z., Bai Q., Zhang X., He Y.S., Lu J., Zou D., Feng C., Dong C.M. Biomimetic Glycopolypeptide Hydrogels with Tunable Adhesion and Microporous Structure for Fast Hemostasis and Highly Efficient Wound Healing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021;31:2105628. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202105628. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

