Disease-Causing TIMP3 Variants and Deep Phenotyping of Two Czech Families with Sorsby Fundus Dystrophy Associated with Novel p.(Tyr152Cys) Mutation
- PMID: 38612555
- PMCID: PMC11011298
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25073744
Disease-Causing TIMP3 Variants and Deep Phenotyping of Two Czech Families with Sorsby Fundus Dystrophy Associated with Novel p.(Tyr152Cys) Mutation
Abstract
We aim to report the ocular phenotype and molecular genetic findings in two Czech families with Sorsby fundus dystrophy and to review all the reported TIMP3 pathogenic variants. Two probands with Sorsby fundus dystrophy and three first-degree relatives underwent ocular examination and retinal imaging, including optical coherence tomography angiography. The DNA of the first proband was screened using a targeted ocular gene panel, while, in the second proband, direct sequencing of the TIMP3 coding region was performed. Sanger sequencing was also used for segregation analysis within the families. All the previously reported TIMP3 variants were reviewed using the American College of Medical Genetics and the Association for Molecular Pathology interpretation framework. A novel heterozygous variant, c.455A>G p.(Tyr152Cys), in TIMP3 was identified in both families and potentially de novo in one. Optical coherence tomography angiography documented in one patient the development of a choroidal neovascular membrane at 54 years. Including this study, 23 heterozygous variants in TIMP3 have been reported as disease-causing. Application of gene-specific criteria denoted eleven variants as pathogenic, eleven as likely pathogenic, and one as a variant of unknown significance. Our study expands the spectrum of TIMP3 pathogenic variants and highlights the importance of optical coherence tomography angiography for early detection of choroidal neovascular membranes.
Keywords: Sorsby fundus dystrophy; TIMP3; choroidal neovascular membrane; optical coherence tomography angiography; pathogenic variants.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

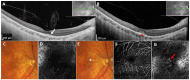
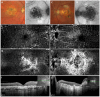
References
-
- Qi J.H., Ebrahem Q., Moore N., Murphy G., Claesson-Welsh L., Bond M., Baker A., Anand-Apte B. A novel function for tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-3 (TIMP3): Inhibition of angiogenesis by blockage of VEGF binding to VEGF receptor-2. Nat. Med. 2003;9:407–415. doi: 10.1038/nm846. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kamei M., Hollyfield J.G. TIMP-3 in Bruch’s membrane: Changes during aging and in age-related macular degeneration. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1999;40:2367–2375. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

