Identification of PTPN12 Phosphatase as a Novel Negative Regulator of Hippo Pathway Effectors YAP/TAZ in Breast Cancer
- PMID: 38612874
- PMCID: PMC11012486
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25074064
Identification of PTPN12 Phosphatase as a Novel Negative Regulator of Hippo Pathway Effectors YAP/TAZ in Breast Cancer
Abstract
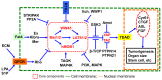
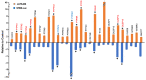
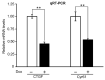
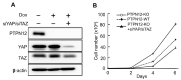
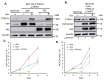
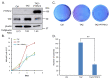
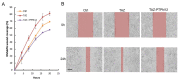
The Hippo pathway plays crucial roles in governing various biological processes during tumorigenesis and metastasis. Within this pathway, upstream signaling stimuli activate a core kinase cascade, involving MST1/2 and LATS1/2, that subsequently phosphorylates and inhibits the transcriptional co-activators YAP and its paralog TAZ. This inhibition modulates the transcriptional regulation of downstream target genes, impacting cell proliferation, migration, and death. Despite the acknowledged significance of protein kinases in the Hippo pathway, the regulatory influence of protein phosphatases remains largely unexplored. In this study, we conducted the first gain-of-functional screen for protein tyrosine phosphatases (PTPs) regulating the Hippo pathway. Utilizing a LATS kinase biosensor (LATS-BS), a YAP/TAZ activity reporter (STBS-Luc), and a comprehensive PTP library, we identified numerous novel PTPs that play regulatory roles in the Hippo pathway. Subsequent experiments validated PTPN12, a master regulator of oncogenic receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs), as a previously unrecognized negative regulator of the Hippo pathway effectors, oncogenic YAP/TAZ, influencing breast cancer cell proliferation and migration. In summary, our findings offer valuable insights into the roles of PTPs in the Hippo signaling pathway, significantly contributing to our understanding of breast cancer biology and potential therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: Hippo pathway; PTPN12; TAZ; YAP; breast cancer; cell migration; cell proliferation; phosphatase; tumor suppressor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
A kinome-wide screen using a NanoLuc LATS luminescent biosensor identifies ALK as a novel regulator of the Hippo pathway in tumorigenesis and immune evasion.FASEB J. 2019 Nov;33(11):12487-12499. doi: 10.1096/fj.201901343R. Epub 2019 Aug 20. FASEB J. 2019. PMID: 31431076 Free PMC article.
-
A gain-of-functional screen identifies the Hippo pathway as a central mediator of receptor tyrosine kinases during tumorigenesis.Oncogene. 2020 Jan;39(2):334-355. doi: 10.1038/s41388-019-0988-y. Epub 2019 Sep 2. Oncogene. 2020. PMID: 31477837
-
Reciprocal regulation of YAP/TAZ by the Hippo pathway and the Small GTPase pathway.Small GTPases. 2020 Jul;11(4):280-288. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2018.1435986. Epub 2018 Apr 20. Small GTPases. 2020. PMID: 29457552 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-hippo kinases: indispensable roles in YAP/TAZ signaling and implications in cancer therapy.Mol Biol Rep. 2023 May;50(5):4565-4578. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-08329-0. Epub 2023 Mar 6. Mol Biol Rep. 2023. PMID: 36877351 Review.
-
Transmembrane protein KIRREL1 regulates Hippo signaling via a feedback loop and represents a therapeutic target in YAP/TAZ-active cancers.Cell Rep. 2022 Aug 30;40(9):111296. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111296. Cell Rep. 2022. PMID: 36044856
Cited by
-
Application of Fluorescence- and Bioluminescence-Based Biosensors in Cancer Drug Discovery.Biosensors (Basel). 2024 Nov 24;14(12):570. doi: 10.3390/bios14120570. Biosensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39727835 Free PMC article. Review.
-
G-quadruplex-dependent transcriptional regulation by molecular condensation in the Bcl3 promoter.Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Aug 27;53(16):gkaf827. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaf827. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025. PMID: 40884402 Free PMC article.
-
Interpretable Machine Learning for Serum-Based Metabolomics in Breast Cancer Diagnostics: Insights from Multi-Objective Feature Selection-Driven LightGBM-SHAP Models.Medicina (Kaunas). 2025 Jun 19;61(6):1112. doi: 10.3390/medicina61061112. Medicina (Kaunas). 2025. PMID: 40572800 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

