The Golgi Apparatus: A Key Player in Innate Immunity
- PMID: 38612929
- PMCID: PMC11012725
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25074120
The Golgi Apparatus: A Key Player in Innate Immunity
Abstract
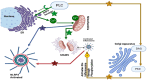
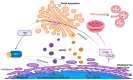
The Golgi apparatus, long recognized for its roles in protein processing and vesicular trafficking, has recently been identified as a crucial contributor to innate immune signaling pathways. This review discusses our expanding understanding of the Golgi apparatus's involvement in initiating and activating these pathways. It highlights the significance of membrane connections between the Golgi and other organelles, such as the endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, endosomes, and autophagosomes. These connections are vital for the efficient transmission of innate immune signals and the activation of effector responses. Furthermore, the article delves into the Golgi apparatus's roles in key immune pathways, including the inflammasome-mediated activation of caspase-1, the cGAS-STING pathway, and TLR/RLR signaling. Overall, this review aims to provide insights into the multifunctional nature of the Golgi apparatus and its impact on innate immunity.
Keywords: Golgi-apparatus; NLRP3-inflammasome; immunology; innate immunity; intracellular-signaling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

