Comparative Efficacy of Different Protein Supplements on Muscle Mass, Strength, and Physical Indices of Sarcopenia among Community-Dwelling, Hospitalized or Institutionalized Older Adults Undergoing Resistance Training: A Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
- PMID: 38612975
- PMCID: PMC11013298
- DOI: 10.3390/nu16070941
Comparative Efficacy of Different Protein Supplements on Muscle Mass, Strength, and Physical Indices of Sarcopenia among Community-Dwelling, Hospitalized or Institutionalized Older Adults Undergoing Resistance Training: A Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Abstract
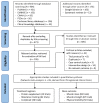
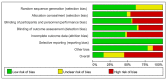
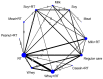
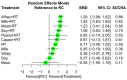
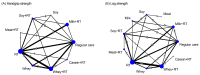
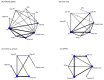
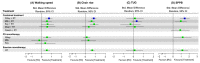
Aging-related sarcopenia exerts harmful impacts on muscle mass, strength, and physical mobility. Protein supplementation has been demonstrated to augment efficacy of resistance training (RT) in elderly. This study compared the relative effects of different protein supplements on muscle mass, strength, and mobility outcomes in middle-aged and older individuals undergoing RT. A comprehensive search of online databases was performed to identify randomized controlled trials (RCTs) examining the efficacy of protein supplement plus RT in untrained community-dwelling adults, hospitalized, or institutionalized residents who suffered acute or chronic health conditions. Network meta-analysis (NMA) was performed using a frequentist method for all analyses. Treatment effects for main outcomes were expressed as standard mean difference (SMD) with 95% confidence interval (CI). We used the surface-under-the cumulative-ranking (SUCRA) scores to rank probabilities of effect estimation among all identified treatments. Meta-regression analyses were performed to identify any relevant moderator of the treatment efficacy and results were expressed as β with 95% credible interval (CrI). We finally included 78 RCTs (5272 participants) for analyses. Among the six protein sources identified in this NMA, namely whey, milk, casein, meat, soy, and peanut, whey supplement yielded the most effective treatments augmenting efficacy of RT on muscle mass (SMD = 1.29, 95% CI: 0.96, 1.62; SUCRA = 0.86), handgrip strength (SMD = 1.46, 95% CI: 0.92, 2.00; SUCRA = 0.85), and walking speed (SMD = 0.73, 95% CI: 0.39, 1.07; SUCRA = 0.84). Participant's health condition, sex, and supplementation dose were significant factors moderating the treatment efficacy on muscle mass (β = 0.74; 95% CrI: 0.22, 1.25), handgrip strength (β = -1.72; 95% CrI: -2.68, -0.77), and leg strength (β = 0.76; 95% CrI: 0.06, 1.47), respectively. Our findings suggest whey protein yields the optimal supplements to counter sarcopenia in older individuals undergoing RT.
Keywords: mobility; muscle mass; protein supplement; resistance exercise; sarcopenia; strength.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

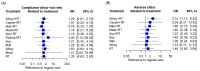
References
-
- Chen L.K., Woo J., Assantachai P., Auyeung T.W., Chou M.Y., Iijima K., Jang H.C., Kang L., Kim M., Kim S., et al. Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia: 2019 Consensus Update on Sarcopenia Diagnosis and Treatment. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2020;21:300–307.e302. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2019.12.012. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Longobucco Y., Krumpoch S., Lauretani F., Angileri V., Sieber C., Marzetti E., Calvani R., Cherubini A., Landi F., Bernabei R., et al. Gait characteristics in community-dwelling older persons with low skeletal muscle mass and low physical performance. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2022;34:1563–1571. doi: 10.1007/s40520-021-02061-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rolland Y., Lauwers-Cances V., Cristini C., Abellan van Kan G., Janssen I., Morley J.E., Vellas B. Difficulties with physical function associated with obesity, sarcopenia, and sarcopenic-obesity in community-dwelling elderly women: The EPIDOS (EPIDemiologie de l’OSteoporose) Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009;89:1895–1900. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.2008.26950. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

