Fabry disease: a rare disorder calling for personalized medicine
- PMID: 38613662
- PMCID: PMC11405476
- DOI: 10.1007/s11255-024-04042-4
Fabry disease: a rare disorder calling for personalized medicine
Abstract
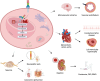
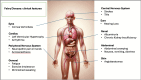
Fabry Disease (FD) is a genetic disease caused by a deficiency in the activity of lysosomal galactosidase A (α-GalA), an enzyme responsible for the catabolism of globotriaosylceramide (Gb3). Since lysosomes are present throughout the body and play a crucial role in catabolism and recycling of cytosolic compounds, FD can affect multiple organs and result in various symptoms, including renal, cardiovascular, neurological, cutaneous, and ophthalmic manifestations. Due to the nonspecific symptoms and the rarity of FD, it is often diagnosed late in life. However, introducing targeted therapies such as enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) and chaperone therapy has significantly improved FD's natural history and prognosis by restoring α-GalA enzyme activity. Despite the advancements, there are limitations to the currently available therapies, which has prompted research into new potential treatments for FD, including alternative forms of enzyme replacement therapy, substrate reduction therapy, mRNA therapy, and genetic therapy. In this review, we analyze the epidemiology, pathophysiology, and treatment of FD, with particular emphasis on promising therapeutic opportunities that could shift the treatment of this rare disease from a standardized to a personalized approach soon.
Keywords: Chaperone therapy; Enzyme replacement therapy; FD; Gene therapy; Treatment; mRNA therapy.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors declare that they have no relevant conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Whybra C, Kampmann C, Krummenauer F, Ries M, Mengel E, Miebach E et al (2004) The mainz severity score index: a new instrument for quantifying the anderson–fabry disease phenotype and the response of patients to enzyme replacement therapy. Clin Genet 65(4):299–307 10.1111/j.1399-0004.2004.00219.x - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical