Identification of a robust biomarker LAPTM4A for glioma based on comprehensive computational biology and experimental verification
- PMID: 38613802
- PMCID: PMC11087115
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.205736
Identification of a robust biomarker LAPTM4A for glioma based on comprehensive computational biology and experimental verification
Abstract
Background: Glioma, a highly invasive and deadly form of human neoplasm, presents a pressing need for the exploration of potential therapeutic targets. While the lysosomal protein transmembrane 4A (LATPM4A) has been identified as a risk factor in pancreatic cancer patients, its role in glioma remains unexplored.
Methods: The analysis of differentially expressed genes (DEG) was conducted from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) glioma dataset and the Genotype Tissue Expression (GTEx) dataset. Through weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA), the key glioma-related genes were identified. Among these, by using Kaplan-Meier (KM) analysis and univariate/multivariate COX methods, LAPTM4A emerged as the most influential gene. Moreover, the bioinformatics methods and experimental verification were employed to analyze its relationships with diagnosis, clinical parameters, epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), metastasis, immune cell infiltration, immunotherapy, drug sensitivity, and ceRNA network.
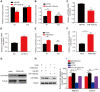
Results: Our findings revealed that LAPTM4A was up-regulated in gliomas and was associated with clinicopathological features, leading to poor prognosis. Furthermore, functional enrichment analysis demonstrated that LATPM4A played a role in the immune system and cancer progression. In vitro experiments indicated that LAPTM4A may influence metastasis through the EMT pathway in glioma. Additionally, we found that LAPTM4A was associated with the tumor microenvironment (TME) and immunotherapy. Notably, drug sensitivity analysis revealed that patients with high LAPTM4A expression were sensitive to doxorubicin, which contributed to a reduction in LAPTM4A expression. Finally, we uncovered the FGD5-AS1-hsa-miR-103a-3p-LAPTM4A axis as a facilitator of glioma progression.
Conclusions: In conclusion, our study identifies LATPM4A as a promising biomarker for prognosis and immune characteristics in glioma.
Keywords: LAPTM4A; ceRNA; glioma; immune infiltration; prognostic biomarker.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
COL8A1 is a potential prognostic biomarker associated with migration, proliferation, and tumor microenvironment in glioma.Exp Cell Res. 2024 Jun 1;439(1):114076. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2024.114076. Epub 2024 May 7. Exp Cell Res. 2024. PMID: 38719174
-
Identification of an epithelial-mesenchymal transition related long non-coding RNA (LncRNA) signature in Glioma.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(1):4016-4031. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1951927. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34288803 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated SLC3A2 associated with poor prognosis and enhanced malignancy in gliomas.Sci Rep. 2024 Jul 9;14(1):15758. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-66484-1. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38977800 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated bioinformatics analysis and experimental validation on malignant progression and immune cell infiltration of LTBP2 in gliomas.BMC Cancer. 2024 Oct 10;24(1):1252. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-12976-2. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39390437 Free PMC article.
-
Transforming brain cancer biomarker research with patinformatics and SWOT analysis.Drug Discov Today. 2025 Mar;30(3):104314. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2025.104314. Epub 2025 Feb 17. Drug Discov Today. 2025. PMID: 39971181 Review.
Cited by
-
Construction of T-Cell-Related Prognostic Risk Models and Prediction of Tumor Immune Microenvironment Regulation in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma via Integrated Analysis of Single-Cell RNA-Seq and Bulk RNA-Seq.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 7;26(6):2384. doi: 10.3390/ijms26062384. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40141028 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Weller M, van den Bent M, Tonn JC, Stupp R, Preusser M, Cohen-Jonathan-Moyal E, Henriksson R, Le Rhun E, Balana C, Chinot O, Bendszus M, Reijneveld JC, Dhermain F, et al., and European Association for Neuro-Oncology (EANO) Task Force on Gliomas. European Association for Neuro-Oncology (EANO) guideline on the diagnosis and treatment of adult astrocytic and oligodendroglial gliomas. Lancet Oncol. 2017; 18:e315–29. 10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30194-8 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Stupp R, Hegi ME, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Taphoorn MJ, Janzer RC, Ludwin SK, Allgeier A, Fisher B, Belanger K, Hau P, Brandes AA, Gijtenbeek J, et al., and European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer Brain Tumour and Radiation Oncology Groups and National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group. Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009; 10:459–66. 10.1016/S1470-2045(09)70025-7 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

