Offspring behavioral outcomes following maternal allergic asthma in the IL-4-deficient mouse
- PMID: 38613873
- PMCID: PMC11088503
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2024.578341
Offspring behavioral outcomes following maternal allergic asthma in the IL-4-deficient mouse
Abstract
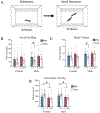
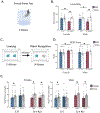
Maternal allergic asthma (MAA) during pregnancy has been associated with increased risk of neurodevelopmental disorders in humans, and rodent studies have demonstrated that inducing a T helper-2-mediated allergic response during pregnancy leads to an offspring behavioral phenotype characterized by decreased social interaction and increased stereotypies. The interleukin (IL)-4 cytokine is hypothesized to mediate the neurobehavioral impact of MAA on offspring. Utilizing IL-4 knockout mice, this study assessed whether MAA without IL-4 signaling would still impart behavioral deficits. C57 and IL-4 knockout female mice were sensitized to ovalbumin, exposed to repeated MAA inductions, and their offspring performed social, cognitive, and motor tasks. Only C57 offspring of MAA dams displayed social and cognitive deficits, while IL-4 knockout mice showed altered motor activity compared with C57 mice. These findings highlight a key role for IL-4 signaling in MAA-induced behavioral deficits and more broadly in normal brain development.
Keywords: Allergic asthma; Behavior; Interleukin-4; Mouse; Offspring; Pregnancy.
Copyright © 2023. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Behavioral impact of maternal allergic-asthma in two genetically distinct mouse strains.Brain Behav Immun. 2017 Jul;63:99-107. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2016.09.007. Epub 2016 Sep 10. Brain Behav Immun. 2017. PMID: 27622677 Free PMC article.
-
Repeated allergic asthma in early versus late pregnancy differentially impacts offspring brain and behavior development.Brain Behav Immun. 2021 Mar;93:66-79. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2020.12.014. Epub 2020 Dec 21. Brain Behav Immun. 2021. PMID: 33358979 Free PMC article.
-
Characterizing the neuroimmune environment of offspring in a novel model of maternal allergic asthma and particulate matter exposure.J Neuroinflammation. 2023 Nov 2;20(1):252. doi: 10.1186/s12974-023-02930-7. J Neuroinflammation. 2023. PMID: 37919762 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal Allergic Asthma Induces Prenatal Neuroinflammation.Brain Sci. 2022 Aug 5;12(8):1041. doi: 10.3390/brainsci12081041. Brain Sci. 2022. PMID: 36009104 Free PMC article.
-
Allergic fetal priming leads to developmental, behavioral and neurobiological changes in mice.Transl Psychiatry. 2015 Apr 7;5(4):e543. doi: 10.1038/tp.2015.40. Transl Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 25849982 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Breach MR, Dye CN, Galan A, & Lenz KM (2022). Prenatal allergic inflammation in rats programs the developmental trajectory of dendritic spine patterning in brain regions associated with cognitive and social behavior. Brain Behav Immun, 102, 279–291. doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2022.02.026 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Breach MR, Dye CN, Joshi A, Platko S, Gilfarb RA, Krug AR, … Lenz KM (2021). Maternal allergic inflammation in rats impacts the offspring perinatal neuroimmune milieu and the development of social play, locomotor behavior, and cognitive flexibility. Brain Behav Immun, 95, 269–286. doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2021.03.025 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

