SHIP inhibition mediates select TREM2-induced microglial functions
- PMID: 38613944
- PMCID: PMC11097602
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molimm.2024.04.002
SHIP inhibition mediates select TREM2-induced microglial functions
Abstract
Microglia play a pivotal role in the pathology of Alzheimer's Disease (AD), with the Triggering Receptor Expressed on Myeloid cells 2 (TREM2) central to their neuroprotective functions. The R47H variant of TREM2 has emerged as a significant genetic risk factor for AD, leading to a loss-of-function phenotype in mouse AD models. This study elucidates the roles of TREM2 in human microglia-like HMC3 cells and the regulation of these functions by SH2-containing inositol-5'-phosphatase 1 (SHIP1). Using stable cell lines expressing wild-type TREM2, the R47H variant, and TREM2-deficient lines, we found that functional TREM2 is essential for the phagocytosis of Aβ, lysosomal capacity, and mitochondrial activity. Notably, the R47H variant displayed increased phagocytic activity towards apoptotic neurons. Introducing SHIP1, known to modulate TREM2 signaling in other cells, revealed its role as a negative regulator of these TREM2-mediated functions. Moreover, pharmacological inhibition of both SHIP1 and its isoform SHIP2 amplified Aβ phagocytosis and lysosomal capacity, independently of TREM2 or SHIP1 expression, suggesting a potential regulatory role for SHIP2 in these functions. The absence of TREM2, combined with the presence of both SHIP isoforms, suppressed mitochondrial activity. However, pan-SHIP1/2 inhibition enhanced mitochondrial function in these cells. In summary, our findings offer a deeper understanding of the relationship between TREM2 variants and SHIP1 in microglial functions, and emphasize the therapeutic potential of targeting the TREM2 and SHIP1 pathways in microglia for neurodegenerative diseases.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Microglia; Phagocytosis; SHIP inhibitors; SHIP1; TREM2.
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest WGK, CP and JDC have patents issued and pending regarding the use of SHIP paralog inhibitors in disease. The other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





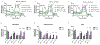
References
-
- Inppl1 expression in the brain - data available from The Human Protein Atlas (v23) - https://www.proteinatlas.org/ENSG00000165458-INPPL1/single+cell+type/brain. 2023.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

