Validation of a commercial ELISA kit to measure 11-oxoetiocholanolone in equine and bovine feces
- PMID: 38616517
- PMCID: PMC11185119
- DOI: 10.1177/10406387241245948
Validation of a commercial ELISA kit to measure 11-oxoetiocholanolone in equine and bovine feces
Abstract
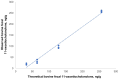
Feces are a noninvasive and easily collectible matrix that may help determine cumulative hormone metabolite concentrations over medium-to-long times. To date, 11-oxoetiocholanolone, an important metabolite of cortisol, has been measured in equine and bovine feces solely by an in-house enzyme immunoassay (EIA). Therefore, we validated the use of a commercial ELISA kit (11-oxoetiocholanolone ELISA kit; Cayman Chemical), which had been validated on sheep feces and human urine, to measure 11-oxoetiocholanolone in feces from 42 horses and 32 bulls. The ELISA kit had good precision (intra- and inter-assay CVs: 5.8% and 11.2% for equine feces; 9.9% and 11.2% for bovine feces, respectively), analytical sensitivity (0.186 ng/mL for both equine and bovine feces), and accuracy (parallelism and recovery tests) in determining 11-oxoetiocholanolone concentrations in feces from both species. We found ranges of 11-oxoetiocholanolone concentrations of 1-109 ng/g in equine feces and 40-302 ng/g in feces of bulls. The Cayman Chemical ELISA kit offers a simple and accessible means of analysis of 11-oxoetiocholanolone in equine and bovine fecal samples.
Keywords: 11-ketoetiocholanolone; cattle; feces; horses; method validation.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interestsThe authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures

References
-
- Bertulat S, et al.. Measurement of fecal glucocorticoid metabolites and evaluation of udder characteristics to estimate stress after sudden dry-off in dairy cows with different milk yields. J Dairy Sci 2013;96:3774–3787. - PubMed
-
- Lexen E, et al.. Monitoring the adrenocortical response to disturbances in sheep by measuring glucocorticoid metabolites in the faeces. Wien Tierarztl Mschr 2008;95:64–71.
-
- Merl S, et al.. Pain causes increased concentrations of glucocorticoid metabolites in horse feces. J Equine Vet Sci 2000;20:586–590.
-
- Möstl E, et al.. Measurement of glucocorticoid metabolite concentrations in faeces of domestic livestock. Zentralbl Veterinarmed A 1999;46:621–631. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

