Efficacy of an aloe vera, chamomile, and thyme cosmetic cream for the prophylaxis and treatment of mild dermatitis induced by radiation therapy in breast cancer patients (the Alantel study)
- PMID: 38616815
- PMCID: PMC11010796
- DOI: 10.1016/j.conctc.2024.101288
Efficacy of an aloe vera, chamomile, and thyme cosmetic cream for the prophylaxis and treatment of mild dermatitis induced by radiation therapy in breast cancer patients (the Alantel study)
Abstract
Objectives: Radiation-induced dermatitis (RD) is one of the most common toxicities in radiation therapy (RT) patients. Corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, and natural products (NPs) have been used as treatment. The objective was to evaluate the efficacy of a NPs-based cream (Alantel®) to reduce the incidence of RD in women with breast cancer undergoing RT treatment.
Design: We conducted a controlled, randomized, double-blind clinical trial.
Setting: Radiation Oncology Unit of the Reina Sofía Hospital and 5 Primary Care centers of the Cordoba and Guadalquivir Health District (Spain).
Interventions: Patients assigned to the experimental group (GTA) were treated with Alantel, while those in the control group (GTE) were treated with a moisturizer and emollient cream.
Main outcome measures: The primary outcome variable was the incidence of RD. RD-free time, duration of RD, quality of life, and product safety were also assessed.
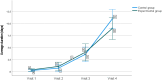
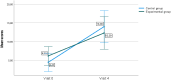
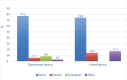
Results: Seventy patients were included in the study, 35 in the GTA and 35 in the GTE. The incidence of RD was lower in the GTA (71.4%) than in the GTE (91.4%) after 4 weeks of follow-up (RR = 0.78; NNT = 5; p < 0.031). The Skindex-29 questionnaire showed differences in the statement: "My skin condition makes it hard to work or do hobbies" (17.1% in the GTE vs. 2.9% in GTA; p = 0.024).
Conclusions: The higher efficacy of Alantel® compared to the control cream in reducing the incidence of RD in women with breast cancer has been demonstrated.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Dermatitis; Radiation therapy.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper. Celia Jimenez Garcia reports financial support, administrative support, article publishing charges, and equipment, drugs, or supplies were provided by Fundación Progreso y Salud. Enrique Villegas Becerril has patent pending to EP23382729-4.
Figures


References
-
- Rao S., Hegde S.K., Baliga-Rao M.P., Palatty P.L., George T., Baliga M.S. An aloe vera-based Cosmeceutical cream Delays and mitigates Ionizing radiation-induced dermatitis in head and neck cancer patients undergoing Curative radiotherapy: a clinical study. Medicines (Basel) 2017;4:44–54. doi: 10.3390/medicines4030044. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

