This is a preprint.
Age-dependent regulation of axoglial interactions and behavior by oligodendrocyte AnkyrinG
- PMID: 38617359
- PMCID: PMC11014615
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.04.01.587609
Age-dependent regulation of axoglial interactions and behavior by oligodendrocyte AnkyrinG
Update in
-
Age-dependent regulation of axoglial interactions and behavior by oligodendrocyte AnkyrinG.Nat Commun. 2024 Dec 30;15(1):10865. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-55209-7. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39738113 Free PMC article.
Abstract
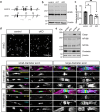
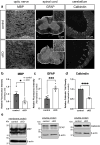
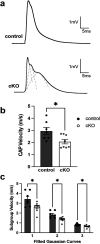
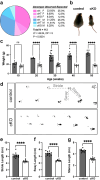
The bipolar disorder (BD) risk gene ANK3 encodes the scaffolding protein AnkyrinG (AnkG). In neurons, AnkG regulates polarity and ion channel clustering at axon initial segments and nodes of Ranvier. Disruption of neuronal AnkG causes BD-like phenotypes in mice. During development, AnkG is also expressed at comparable levels in oligodendrocytes and facilitates the efficient assembly of paranodal junctions. However, the physiological roles of glial AnkG in the mature nervous system, and its contributions to BD-like phenotypes, remain unexplored. Here, we generated oligodendroglia-specific AnkG conditional knockout mice and observed the destabilization of axoglial interactions in aged but not young adult mice. In addition, these mice exhibited profound histological, electrophysiological, and behavioral pathophysiologies. Unbiased translatomic profiling revealed potential compensatory machineries. These results highlight the critical functions of glial AnkG in maintaining proper axoglial interactions throughout aging and suggests a previously unrecognized contribution of oligodendroglial AnkG to neuropsychiatric disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
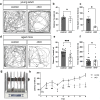

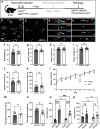
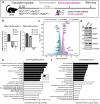
References
-
- Bhat M. A. et al. Axon-glia interactions and the domain organization of myelinated axons requires neurexin IV/Caspr/Paranodin. Neuron 30, 369–383. (2001). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
