This is a preprint.
APOBEC shapes tumor evolution and age at onset of lung cancer in smokers
- PMID: 38617360
- PMCID: PMC11014539
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.04.02.587805
APOBEC shapes tumor evolution and age at onset of lung cancer in smokers
Update in
-
APOBEC affects tumor evolution and age at onset of lung cancer in smokers.Nat Commun. 2025 May 21;16(1):4711. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-59923-8. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40394004 Free PMC article.
Abstract
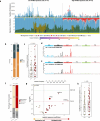
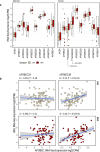
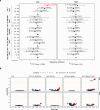
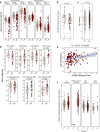
APOBEC enzymes are part of the innate immunity and are responsible for restricting viruses and retroelements by deaminating cytosine residues1,2. Most solid tumors harbor different levels of somatic mutations attributed to the off-target activities of APOBEC3A (A3A) and/or APOBEC3B (A3B)3-6. However, how APOBEC3A/B enzymes shape the tumor evolution in the presence of exogenous mutagenic processes is largely unknown. Here, by combining deep whole-genome sequencing with multi-omics profiling of 309 lung cancers from smokers with detailed tobacco smoking information, we identify two subtypes defined by low (LAS) and high (HAS) APOBEC mutagenesis. LAS are enriched for A3B-like mutagenesis and KRAS mutations, whereas HAS for A3A-like mutagenesis and TP53 mutations. Unlike APOBEC3A, APOBEC3B expression is strongly associated with an upregulation of the base excision repair pathway. Hypermutation by unrepaired A3A and tobacco smoking mutagenesis combined with TP53-induced genomic instability can trigger senescence7, apoptosis8, and cell regeneration9, as indicated by high expression of pulmonary healing signaling pathway, stemness markers and distal cell-of-origin in HAS. The expected association of tobacco smoking variables (e.g., time to first cigarette) with genomic/epigenomic changes are not observed in HAS, a plausible consequence of frequent cell senescence or apoptosis. HAS have more neoantigens, slower clonal expansion, and older age at onset compared to LAS, particularly in heavy smokers, consistent with high proportions of newly generated, unmutated cells and frequent immuno-editing. These findings show how heterogeneity in mutational burden across co-occurring mutational processes and cell types contributes to tumor development, with important clinical implications.
Conflict of interest statement
ETHICS DECLARATIONS LBA is a compensated consultant and has equity interest in io9, LLC. His spouse is an employee of Biotheranostics, Inc. LBA is also an inventor of a US Patent 10,776,718 for source identification by non-negative matrix factorization. ENB and LBA declare U.S. provisional patent applications with serial numbers 63/289,601 and 63/269,033. LBA also declares U.S. provisional patent applications with serial numbers: 63/366,392; 63/367,846; and 63/412,835. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
APOBEC affects tumor evolution and age at onset of lung cancer in smokers.Nat Commun. 2025 May 21;16(1):4711. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-59923-8. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40394004 Free PMC article.
-
Tobacco smoke carcinogens exacerbate APOBEC mutagenesis and carcinogenesis.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2025 Jun 3:rs.3.rs-5843684. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-5843684/v1. Res Sq. 2025. PMID: 40502742 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Can a Liquid Biopsy Detect Circulating Tumor DNA With Low-passage Whole-genome Sequencing in Patients With a Sarcoma? A Pilot Evaluation.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025 Jan 1;483(1):39-48. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003161. Epub 2024 Jun 21. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025. PMID: 38905450
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Smoking cessation medicines and e-cigarettes: a systematic review, network meta-analysis and cost-effectiveness analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2021 Oct;25(59):1-224. doi: 10.3310/hta25590. Health Technol Assess. 2021. PMID: 34668482
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
