The frontier of tungsten oxide nanostructures in electronic applications
- PMID: 38617562
- PMCID: PMC11015465
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109535
The frontier of tungsten oxide nanostructures in electronic applications
Abstract
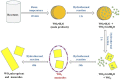
Electrochromic (EC) glazing has garnered significant attention recently as a crucial solution for enhancing energy efficiency in future construction and automotive sectors. EC glazing could significantly reduce the energy usage of buildings compared to traditional blinds and glazing. Despite their commercial availability, several challenges remain, including issues with switching time, leakage of electrolytes, production costs, etc. Consequently, these areas demand more attention and further studies. Among inorganic-based EC materials, tungsten oxide nanostructures are essential due to its outstanding advantages such as low voltage demand, high coloration coefficient, large optical modulation range, and stability. This review will summarize the principal design and mechanism of EC device fabrication. It will highlight the current gaps in understanding the mechanism of EC theory, discuss the progress in material development for EC glazing, including various solutions for improving EC materials, and finally, introduce the latest advancements in photo-EC devices that integrate photovoltaic and EC technologies.
Keywords: Electronic materials; Materials chemistry.
© 2024 Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures











References
-
- Alturki A. The Global Carbon Footprint and How New Carbon Mineralization Technologies Can Be Used to Reduce CO2 Emissions. ChemEngineering. 2022;6:44. doi: 10.3390/chemengineering6030044. - DOI
-
- Huang L., Krigsvoll G., Johansen F., Liu Y., Zhang X. Carbon emission of global construction sector. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018;81:1906–1916. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2017.06.001. - DOI
-
- Granqvist C.G., Arvizu M.A., Bayrak Pehlivan İ., Qu H.Y., Wen R.T., Niklasson G.A. Electrochromic materials and devices for energy efficiency and human comfort in buildings: A critical review. Electrochim. Acta. 2018;259:1170–1182. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2017.11.169. - DOI
-
- Ke Y., Chen J., Lin G., Wang S., Zhou Y., Yin J., Lee P.S., Long Y. Smart Windows: Electro-Thermo-Mechano-Photochromics, and Beyond. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019;9 doi: 10.1002/aenm.201902066. - DOI
-
- Nundy S., Mesloub A., Alsolami B.M., Ghosh A. Electrically actuated visible and near-infrared regulating switchable smart window for energy positive building: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021;301 doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126854. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

