Advancements in Stimulus-Responsive Co-Delivery Nanocarriers for Enhanced Cancer Immunotherapy
- PMID: 38617801
- PMCID: PMC11012697
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S454004
Advancements in Stimulus-Responsive Co-Delivery Nanocarriers for Enhanced Cancer Immunotherapy
Abstract
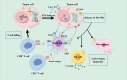
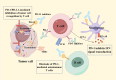
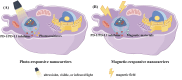
Cancer immunotherapy has emerged as a novel therapeutic approach against tumors, with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) making significant clinical practice. The traditional ICIs, PD-1 and PD-L1, augment the cytotoxic function of T cells through the inhibition of tumor immune evasion pathways, ultimately leading to the initiation of an antitumor immune response. However, the clinical implementation of ICIs encounters obstacles stemming from the existence of an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment and inadequate infiltration of CD8+T cells. Considerable attention has been directed towards advancing immunogenic cell death (ICD) as a potential solution to counteract tumor cell infiltration and the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment. This approach holds promise in transforming "cold" tumors into "hot" tumors that exhibit responsiveness to antitumor. By combining ICD with ICIs, a synergistic immune response against tumors can be achieved. However, the combination of ICD inducers and PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors is hindered by issues such as poor targeting and uncontrolled drug release. An advantageous solution presented by stimulus-responsive nanocarrier is integrating the physicochemical properties of ICD inducers and PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors, facilitating precise delivery to specific tissues for optimal combination therapy. Moreover, these nanocarriers leverage the distinct features of the tumor microenvironment to accomplish controlled drug release and regulate the kinetics of drug delivery. This article aims to investigate the advancement of stimulus-responsive co-delivery nanocarriers utilizing ICD and PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors. Special focus is dedicated to exploring the advantages and recent advancements of this system in enabling the combination of ICIs and ICD inducers. The molecular mechanisms of ICD and ICIs are concisely summarized. In conclusion, we examine the potential research prospects and challenges that could greatly enhance immunotherapeutic approaches for cancer treatment.
Keywords: antitumor therapy; co-delivery; immune-checkpoint inhibitors; immunogenic cell death; stimulus-responsive nanocarriers.
© 2024 Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Nanomicelle protects the immune activation effects of Paclitaxel and sensitizes tumors to anti-PD-1 Immunotherapy.Theranostics. 2020 Jul 9;10(18):8382-8399. doi: 10.7150/thno.45391. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 32724476 Free PMC article.
-
Immunogenic Cell Death Inducers in Cancer Immunotherapy to Turn Cold Tumors into Hot Tumors.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 14;26(4):1613. doi: 10.3390/ijms26041613. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40004078 Free PMC article.
-
Peptide vaccine-conjugated mesoporous carriers synergize with immunogenic cell death and PD-L1 blockade for amplified immunotherapy of metastatic spinal.J Nanobiotechnology. 2021 Aug 12;19(1):243. doi: 10.1186/s12951-021-00975-5. J Nanobiotechnology. 2021. PMID: 34384429 Free PMC article.
-
Combination Cancer Immunotherapy of Nanoparticle-Based Immunogenic Cell Death Inducers and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors.Int J Nanomedicine. 2021 Feb 22;16:1435-1456. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S285999. eCollection 2021. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021. PMID: 33654395 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors.Int Immunopharmacol. 2023 Feb;115:109638. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.109638. Epub 2022 Dec 30. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36587500 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting immune checkpoints in hepatocellular carcinoma therapy: toward combination strategies with curative potential.Exp Hematol Oncol. 2025 May 2;14(1):65. doi: 10.1186/s40164-025-00636-5. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40317077 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanoscale Porphyrin-Based Metal-Organic Frameworks for Enhanced Radiotherapy-Radiodynamic Therapy: A Comprehensive Review.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Jul 4;17(7):883. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17070883. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40733092 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

