Capacity for the management of kidney failure in the International Society of Nephrology Middle East region: report from the 2023 ISN Global Kidney Health Atlas (ISN-GKHA)
- PMID: 38618498
- PMCID: PMC11010631
- DOI: 10.1016/j.kisu.2024.01.009
Capacity for the management of kidney failure in the International Society of Nephrology Middle East region: report from the 2023 ISN Global Kidney Health Atlas (ISN-GKHA)
Abstract
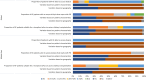
The highest financial and symptom burdens and the lowest health-related quality-of-life scores are seen in people with kidney failure. A total of 11 countries in the International Society of Nephrology (ISN) Middle East region responded to the ISN-Global Kidney Health Atlas. The prevalence of chronic kidney disease (CKD) in the region ranged from 4.9% in Yemen to 12.2% in Lebanon, whereas prevalence of kidney failure treated with dialysis or transplantation ranged from 152 per million population (pmp) in the United Arab Emirates to 869 pmp in Kuwait. Overall, the incidence of kidney transplantation was highest in Saudi Arabia (20.2 pmp) and was lowest in Oman (2.2 pmp). Chronic hemodialysis (HD) and peritoneal dialysis (PD) services were available in all countries, whereas kidney transplantation was available in most countries of the region. Public government funding that makes acute dialysis, chronic HD, chronic PD, and kidney transplantation medications free at the point of delivery was available in 54.5%, 72.7%, 54.5%, and 54.5% of countries, respectively. Conservative kidney management was available in 45% of countries. Only Oman had a CKD registry; 7 countries (64%) had dialysis registries, and 8 (73%) had kidney transplantation registries. The ISN Middle East region has a high burden of kidney disease and multiple challenges to overcome. Prevention and detection of kidney disease can be improved by the design of tailored guidelines, allocation of additional resources, improvement of early detection at all levels of care, and implementation of sustainable health information systems.
Keywords: Global Kidney Health Atlas; ISN; epidemiology; kidney failure; kidney replacement therapy; the Middle East.
© 2024 International Society of Nephrology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Comment in
-
Variations in kidney care management and access: regional assessments of the 2023 International Society of Nephrology Global Kidney Health Atlas (ISN-GKHA).Kidney Int Suppl (2011). 2024 Apr;13(1):1-5. doi: 10.1016/j.kisu.2023.12.001. Epub 2024 Apr 8. Kidney Int Suppl (2011). 2024. PMID: 38619132 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Jager K.J., Kovesdy C., Langham R., et al. A single number for advocacy and communication—worldwide more than 850 million individuals have kidney diseases. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2019;34:1803–1805. - PubMed
-
- Alasfar S., Alashavi H., Nasan K.H., et al. Improving and maintaining quality of hemodialysis in areas affected by war: a call to action! Kidney Int. 2023;103:817–820. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

