Global Stillbirth Policy Review - Outcomes And Implications Ahead of the 2030 Sustainable Development Goal Agenda
- PMID: 38618824
- PMCID: PMC10590256
- DOI: 10.34172/ijhpm.2023.7391
Global Stillbirth Policy Review - Outcomes And Implications Ahead of the 2030 Sustainable Development Goal Agenda
Abstract
Background: Globally, data on stillbirth is limited. A call to action has been issued to governments to address the data gap by strengthening national policies and strategies to drive urgent action on stillbirth reduction. This study aims to understand the policy environment for stillbirths to advance stillbirth recording and reporting in data systems.
Methods: A systematic three-step process (survey tool examination, identifying relevant study questions, and reviewing country responses to the survey and national documents) was taken to review country responses to the global 2018-2019 World Health Organization (WHO) Reproductive, Maternal, Neonatal, Child and Adolescent Health (RMNCAH) Policy Survey. Policy Survey responses were reviewed to identify if and how stillbirths were included in national documents. This paper uses descriptive analyses to identify and describe the relationship between multiple variables.
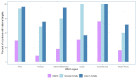
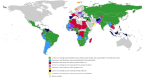
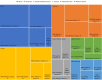
Results: Responses from 155 countries to the survey were analysed, and over 800 national policy documents submitted by countries in English reviewed. Fewer than one-fifth of countries have an established stillbirth rate (SBR) target, with higher percentages reported for under-5 (71.0%) and neonatal mortality (68.5%). Two-thirds (65.8%) of countries reported a national maternal death review panel. Less than half (43.9%) of countries have a national policy that requires stillbirths to be reviewed. Two-thirds of countries have a national policy requiring review of neonatal deaths. WHO websites and national health statistics reports are the common data sources for stillbirth estimates. Countries that are signatories to global initiatives on stillbirth reduction have established national targets. Globally, nearly all countries (94.8%) have a national policy that requires every death to be registered. However, 45.5% of reviewed national policy documents made mention of registering stillbirths. Only 5 countries had national policy documents recommending training of health workers in filling out death certificates using the International Classification of Diseases (ICD)-10 for stillbirths.
Conclusion: The current policy environment in countries is not supportive for identifying stillbirths and recording causes of death. This is likely to contribute to slow progress in stillbirth reduction. The paper proposes policy recommendations to make every baby count.
Keywords: Fetal Death; Health Policies; Health Systems; Measurement; Perinatal Health; Stillbirths.
© 2023 The Author(s); Published by Kerman University of Medical Sciences This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- UNICEF, World Health Organization, World Bank Group, United Nations. A Neglected Tragedy: The Global Burden of Stillbirths. Report of the UN Inter-Agency Group for Child Mortality Estimation. UNICEF, World Health Organization, World Bank Group, United Nations; 2020.
-
- World Health Organization (WHO), UNICEF. Every Newborn: An Action Plan to End Preventable Deaths. Luxembourg: WHO, UNICEF; 2014.
-
- World Health Organization (WHO), United Nations. Global Strategy for Women’s, Children’s and Adolescents Health 2016-2030. Geneva: WHO; 2016.
-
- World Health Organization (WHO). Quality, Equity, Dignity: The Network to Improve Quality of Care for Maternal, Newborn and Child Health. WHO; 2017.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous