Sensitive methods for detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA
- PMID: 38620918
- PMCID: PMC8283572
- DOI: 10.1016/bs.mim.2021.06.001
Sensitive methods for detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA
Abstract
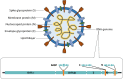
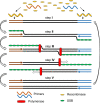
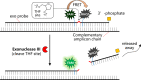
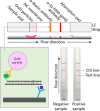
The occurrence of the COVID-19 pandemic caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus since the end of 2019 has significantly affected the entire world. Now SARS-CoV-2 diagnostic tests are not only required for screening of suspected infected people for their medical treatment, but have also become a routine diagnosis for all people at a place where new cases have emerged in order to control spread of the disease from that region. For these reasons, sensitive methods for detection of SARS-CoV-2 are highly needed in order to avoid undetected infections. In addition, sample pooling that uses pooled specimens has been routinely employed as a time- and cost-effective strategy for community monitoring of SARS-CoV-2. In this regard, the content of each viral RNA sample of an individual will be further diluted in detection; therefore, higher detection sensitivity would be rather preferred. Among nucleic acid-based detection methods, isothermal nucleic acid amplifications are considered quite promising because they typically take less time to complete the test (even less than 20 min) without the need of thermal cycles. Hence, it does not necessitate the use of highly costly real-time PCR machines. According to recently published isothermal nucleic acid amplification methods, the reverse transcription recombinase polymerase amplification (RT-RPA) approach shows outstanding sensitivity with up to single-copy sensitivity in a test reaction. This chapter will mainly focus on how to employ RT-RPA technology to sensitively detect SARS-CoV-2 RNA. Besides, recently published RT-RPA based detection methods will be summarized and compared regarding their detection parameters and the primers and probes being used. In addition, we will also highlight the key considerations on how to design an ultrasensitive RT-RPA assay and the precautions needed to conduct the assay. Moreover, based on our recent report, we will also detail the methods we developed to detect SARS-CoV-2 RNA using modified RT-RPA, or RT-ERA, with single-copy sensitivity and the possible extensions beyond this method.
Keywords: Exo probe; Lateral flow; Nfo probe; RT-RPA; SARS-CoV-2 RNA; Single-copy sensitivity.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Rapid and Visual Detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA Based on Reverse Transcription-Recombinase Polymerase Amplification with Closed Vertical Flow Visualization Strip Assay.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Feb 14;11(1):e0296622. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02966-22. Epub 2023 Jan 9. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 36622165 Free PMC article.
-
Isothermal recombinase polymerase amplification-lateral flow detection of SARS-CoV-2, the etiological agent of COVID-19.J Virol Methods. 2021 Oct;296:114227. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2021.114227. Epub 2021 Jul 2. J Virol Methods. 2021. PMID: 34224752 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid Detection of SARS-CoV-2 by Low Volume Real-Time Single Tube Reverse Transcription Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Using an Exo Probe with an Internally Linked Quencher (Exo-IQ).Clin Chem. 2020 Aug 1;66(8):1047-1054. doi: 10.1093/clinchem/hvaa116. Clin Chem. 2020. PMID: 32384153 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody tests for identification of current and past infection with SARS-CoV-2.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jun 25;6(6):CD013652. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013652. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Nov 17;11:CD013652. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013652.pub2. PMID: 32584464 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Rapid, point-of-care antigen and molecular-based tests for diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Mar 24;3(3):CD013705. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013705.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jul 22;7:CD013705. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013705.pub3. PMID: 33760236 Free PMC article. Updated.
Cited by
-
Molecular Diagnosis of COVID-19; Biosafety and Pre-analytical Recommendations.Iran J Pathol. 2023 Summer;18(3):244-256. doi: 10.30699/IJP.2023.1988405.3061. Epub 2023 Jul 16. Iran J Pathol. 2023. PMID: 37942195 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnostic performances of four commercially available assays for the identification of SARS-CoV-2, influenza type A/B virus and RSV.Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2023 Aug;106(4):115970. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2023.115970. Epub 2023 Apr 24. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 37290260 Free PMC article.
-
Immunological insights: assessing immune parameters in medical professionals exposed to SARS-CoV-2.BMC Infect Dis. 2024 Aug 26;24(1):865. doi: 10.1186/s12879-024-09772-5. BMC Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 39187767 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Behrmann O., Bachmann I., Spiegel M., Schramm M., Abd El Wahed A., Dobler G., et al. Rapid detection of SARS-CoV-2 by low volume real-time single tube reverse transcription recombinase polymerase amplification using an exo probe with an internally linked quencher (Exo-IQ) Clinical Chemistry. 2020;66(8):1047–1054. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
