Effect of different positive end expiratory pressure levels on optic nerve sheath diameter in patients with or without midline shift who are undergoing supratentorial craniotomy
- PMID: 38622368
- PMCID: PMC11018676
- DOI: 10.1007/s00701-024-06067-1
Effect of different positive end expiratory pressure levels on optic nerve sheath diameter in patients with or without midline shift who are undergoing supratentorial craniotomy
Abstract
Purpose: In general, high levels of PEEP application is avoided in patients undergoing craniotomy to prevent a rise in ICP. But that approach would increase the risk of secondary brain injury especially in hypoxemic patients. Because the optic nerve sheath is distensible, a rise in ICP is associated with an increase in the optic nerve sheath diameter (ONSD). The cutoff value for elevated ICP assessed by ONSD is between 5.6 and 6.3 mm. We aimed to evaluate the effect of different PEEP levels on ONSD and compare the effect of different PEEP levels in patients with and without intracranial midline shift.
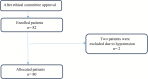
Methods: This prospective observational study was performed in aged 18-70 years, ASA I-III, 80 patients who were undergoing supratentorial craniotomy. After the induction of general anesthesia, the ONSD's were measured by the linear transducer from 3 mm below the globe at PEEP values of 0-5-10 cmH2O. The ONSD were compered between patients with (n = 7) and without midline shift (n = 73) at different PEEP values.
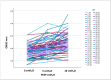
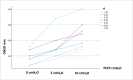
Results: The increases in ONSD due to increase in PEEP level were determined (p < 0.001). No difference was found in the comparison of ONSD between patients with and without midline shift in different PEEP values (p = 0.329, 0.535, 0.410 respectively). But application of 10 cmH2O PEEP in patients with a midline shift increased the mean ONSD value to 5.73 mm. This value is roughly 0.1 mm higher than the lower limit of the ONSD cutoff value.
Conclusions: The ONSD in adults undergoing supratentorial tumor craniotomy, PEEP values up to 5 cmH2O, appears not to be associated with an ICP increase; however, the ONSD exceeded the cutoff for increased ICP when a PEEP of 10 cmH2O was applied in patients with midline shift.
Keywords: Craniotomy; Intracranial pressure, Elevated; Optic nerve sheath; Positive end expiratory pressure.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Correlation of the transorbital ultrasonographic optic nerve sheath diameter with intracranial pressure measured intraoperatively in infants with hydrocephalus.J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2024 Jan 12;33(4):334-342. doi: 10.3171/2023.12.PEDS23273. Print 2024 Apr 1. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 38215445
-
Optic nerve sheath diameter correlates with both success and failure of hydrocephalus treatment in pediatric patients with pineal region lesions.Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2024 May 28;166(1):236. doi: 10.1007/s00701-024-06122-x. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2024. PMID: 38805061
-
Ultrasonographic Assessment of Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter as a Screening Tool for Intracranial Hypertension in Traumatic Brain Injury.World Neurosurg. 2024 Dec;192:e42-e48. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2024.08.111. Epub 2024 Aug 27. World Neurosurg. 2024. PMID: 39209251
-
The role of optic nerve sheath ultrasonography in increased intracranial pressure: A systematic review and meta analysis.J Neurol Sci. 2023 Nov 15;454:120853. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2023.120853. Epub 2023 Oct 30. J Neurol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37925899
-
Diagnostic Accuracy of Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter Measurement by Ultrasonography for Noninvasive Estimation of Intracranial Hypertension in Traumatic Brain Injury: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Neurosurgery. 2024 Nov 8;97(1):45-56. doi: 10.1227/neu.0000000000003273. Neurosurgery. 2024. PMID: 39513703
References
-
- Aspide R, Bertolini G, Albini Riccioli L, Mazzatenta D, Palandri G, Biasucci DG (2020) A proposal for a new protocol for sonographic assessment of the optic nerve sheath diameter: the CLOSED protocol. Neurocrit Care 32(1):327–332 - PubMed
-
- Berhanu D, Ferreira JC, Abegao Pinto L, Aguiar de Sousa D, Lucas Neto L, Tavares Ferreira J (2023) The role of optic nerve sheath ultrasonography in increased intracranial pressure: a systematic review and meta analysis. J Neurol Sci 454:120853 - PubMed
-
- Caricato A, Conti G, Della Corte F, Mancino A, Santilli F, Sandroni C et al (2005) Effects of PEEP on the intracranial system of patients with head injury and subarachnoid hemorrhage: the role of respiratory system compliance. J Trauma 58(3):571–576 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources