Comparison of early patient-reported outcomes between uniportal thoracoscopic segmentectomy and wedge resection for peripheral small-sized non-small-cell lung cancer
- PMID: 38622650
- PMCID: PMC11017554
- DOI: 10.1186/s13019-024-02635-9
Comparison of early patient-reported outcomes between uniportal thoracoscopic segmentectomy and wedge resection for peripheral small-sized non-small-cell lung cancer
Abstract
Background: Analysis of patient-reported outcomes (PROs) offers valuable insights into distinguishing the effects of closely related medical procedures from the patient's perspective. In this study we compared symptom burden in patients undergoing uniportal thoracoscopic segmentectomy and wedge resection for peripheral small-sized non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
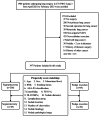
Methods: This study included patients with peripheral NSCLC from an ongoing longitudinal prospective cohort study (CN-PRO-Lung 3) who underwent segmentectomy or wedge resection with tumor diameter ≤ 2 cm and consolidation tumor ratio (CTR) ≤ 0.5. PROs data were collected using the Perioperative Symptom Assessment for Lung Surgery questionnaire pre-operatively, daily post-surgery up to the fourth hospitalization day, and weekly post-discharge up to the fourth week. Propensity score matching and a generalized estimation equation model were employed to compare symptom severity. In addition, short-term clinical outcomes were compared.
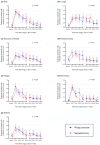
Results: In total, data of 286 patients (82.4%) undergoing segmentectomy and 61 patients (17.6%) undergoing wedge resection were extracted from the cohort. No statistically significant differences were found in the proportion of moderate-to-severe symptoms and mean scores for pain, cough, shortness of breath, disturbed sleep, fatigue, drowsiness, and distress during the 4-day postoperative hospitalization or the 4-week post-discharge period before or after matching (all p > 0.05). Compared with segmentectomy, wedge resection showed better short-term clinical outcomes, including shorter operative time (p = 0.001), less intraoperative bleeding (p = 0.046), and lower total hospital costs (p = 0.002).
Conclusions: The study findings indicate that uniportal thoracoscopic segmentectomy and wedge resection exert similar early postoperative symptom burden in patients with peripheral NSCLC (tumor diameter ≤ 2 cm and CTR ≤ 0.5).
Clinical trial registration: Not applicable.
Keywords: Non-small cell lung carcinoma; Patient-reported outcomes; Pneumonectomy.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Early Postoperative Patient-Reported Outcomes After Thoracoscopic Segmentectomy Versus Lobectomy for Small-Sized Peripheral Non-small-cell Lung Cancer.Ann Surg Oncol. 2022 Jan;29(1):547-556. doi: 10.1245/s10434-021-10946-7. Epub 2021 Nov 6. Ann Surg Oncol. 2022. PMID: 34743281
-
Comparison of early postoperative patient-reported outcomes after multiportal robotic-assisted thoracoscopic surgery and uniportal video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery for non-small cell lung cancer.Eur J Surg Oncol. 2024 Sep;50(9):108481. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2024.108481. Epub 2024 Jun 12. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38959845
-
Comparison of Early Functional Recovery Following Triportal Robot-Assisted and Uniportal Video-Assisted Segmentectomy in Patients With Early-Stage Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Propensity Score-Matched Analysis.Thorac Cancer. 2025 Mar;16(5):e70041. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.70041. Thorac Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40074689 Free PMC article.
-
Oncological Outcomes of Lobar Resection, Segmentectomy, and Wedge Resection for T1a Non-Small-Cell Lung Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2020 Autumn;32(3):582-590. doi: 10.1053/j.semtcvs.2019.08.004. Epub 2019 Aug 9. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2020. PMID: 31401180
-
Sublobar Resection of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Wedge Resection vs. Segmentectomy.Curr Oncol. 2024 Apr 29;31(5):2497-2507. doi: 10.3390/curroncol31050187. Curr Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38785468 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Persistent cough after pulmonary resection: Minor issue, major hurdle.Heliyon. 2024 May 18;10(10):e31338. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31338. eCollection 2024 May 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38826748 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early postoperative patient-reported outcomes in thoracoscopic segmentectomy: a comparative study of non-intubated anesthesia versus intubated general anesthesia.Front Oncol. 2025 Jul 7;15:1602812. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1602812. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40692867 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous