The multiple roles of viral 3Dpol protein in picornavirus infections
- PMID: 38622757
- PMCID: PMC11020597
- DOI: 10.1080/21505594.2024.2333562
The multiple roles of viral 3Dpol protein in picornavirus infections
Abstract
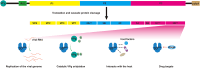
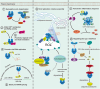
The Picornaviridae are a large group of positive-sense, single-stranded RNA viruses, and most research has focused on the Enterovirus genus, given they present a severe health risk to humans. Other picornaviruses, such as foot-and-mouth disease virus (FMDV) and senecavirus A (SVA), affect agricultural production with high animal mortality to cause huge economic losses. The 3Dpol protein of picornaviruses is widely known to be used for genome replication; however, a growing number of studies have demonstrated its non-polymerase roles, including modulation of host cell biological processes, viral replication complex assembly and localization, autophagy, and innate immune responses. Currently, there is no effective vaccine to control picornavirus diseases widely, and clinical therapeutic strategies have limited efficiency in combating infections. Many efforts have been made to develop different types of drugs to prohibit virus survival; the most important target for drug development is the virus polymerase, a necessary element for virus replication. For picornaviruses, there are also active efforts in targeted 3Dpol drug development. This paper reviews the interaction of 3Dpol proteins with the host and the progress of drug development targeting 3Dpol.
Keywords: 3Dpol; Picornaviruses; RNA-dependent RNA polymerase; RdRp inhibitor; virus-host interaction.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures



Similar articles
-
Heterogeneous Nuclear Ribonucleoprotein L Negatively Regulates Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus Replication through Inhibition of Viral RNA Synthesis by Interacting with the Internal Ribosome Entry Site in the 5' Untranslated Region.J Virol. 2020 May 4;94(10):e00282-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00282-20. Print 2020 May 4. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32161169 Free PMC article.
-
Non-Nucleoside Inhibitors Decrease Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus Replication by Blocking the Viral 3Dpol.Viruses. 2022 Dec 30;15(1):124. doi: 10.3390/v15010124. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 36680163 Free PMC article.
-
Residues within the Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus 3Dpol Nuclear Localization Signal Affect Polymerase Fidelity.J Virol. 2020 Aug 17;94(17):e00833-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00833-20. Print 2020 Aug 17. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32581111 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple functions of the nonstructural protein 3D in picornavirus infection.Front Immunol. 2024 Apr 2;15:1365521. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1365521. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38629064 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances and Breakthroughs in IRES-Directed Translation and Replication of Picornaviruses.mBio. 2023 Apr 25;14(2):e0035823. doi: 10.1128/mbio.00358-23. Epub 2023 Mar 20. mBio. 2023. PMID: 36939331 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Multi-Model Machine Learning Framework for Identifying Raloxifene as a Novel RNA Polymerase Inhibitor from FDA-Approved Drugs.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025 Apr 28;47(5):315. doi: 10.3390/cimb47050315. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40699714 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Transcriptomics Analysis of Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus-Infected Cell Model Systems.Vet Sci. 2025 Feb 1;12(2):107. doi: 10.3390/vetsci12020107. Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40005867 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism research of Punicalagin in treating representative strains of enterovirus A and B types based on systems pharmacology and experimental validation.Virol J. 2025 Jul 9;22(1):229. doi: 10.1186/s12985-025-02845-0. Virol J. 2025. PMID: 40634970 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
