Single-dose ibuprofen induced Stevens-Johnson Syndrome
- PMID: 38623360
- PMCID: PMC11017452
- DOI: 10.1002/ccr3.8574
Single-dose ibuprofen induced Stevens-Johnson Syndrome
Abstract
Key clinical message: Ibuprofen single dose may rarely induce Stevens-Johnson Syndrome, emphasizing the vital need for heightened vigilance in healthcare and public awareness for safer medication practices.
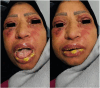
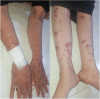
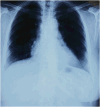
Abstract: Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS) is a severe and potentially life-threatening skin disorder associated with certain medications, including ibuprofen. We present a case of a 45-year-old woman who developed SJS following a single dose of ibuprofen. Despite its rarity, this case underscores the importance of heightened vigilance in healthcare and public awareness regarding the potential risks of commonly used medications. Prompt recognition of SJS symptoms and immediate medical intervention are crucial for patient outcomes. Healthcare providers should exercise caution when prescribing ibuprofen, particularly in patients with a history of adverse drug reactions. This case emphasizes the need for ongoing monitoring, patient education, and informed decision-making to promote medication safety and optimal patient care.
Keywords: acute medicine; critical care medicine; dermatology; immunology; pharmacology and pharmacy.
© 2024 The Authors. Clinical Case Reports published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures


References
-
- Pieper S. Fluoroquinolone‐associated disability (FQAD)‐pathogenesis, diagnostics, therapy and diagnostic criteria: side‐effects of Fluoroquinolones. Springer Nature; 2021.
-
- Rainsford KD. Ibuprofen: pharmacology, efficacy and safety. Inflammopharmacology. 2009;17:275‐342. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

