The ACE2/Ang-(1-7)/MasR axis alleviates brain injury after cardiopulmonary resuscitation in rabbits by activating PI3K/Akt signaling
- PMID: 38623573
- PMCID: PMC11017183
- DOI: 10.1515/tnsci-2022-0334
The ACE2/Ang-(1-7)/MasR axis alleviates brain injury after cardiopulmonary resuscitation in rabbits by activating PI3K/Akt signaling
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to "The ACE2/Ang-(1-7)/MasR axis alleviates brain injury after cardiopulmonary resuscitation in rabbits by activating PI3K/Akt signaling".Transl Neurosci. 2024 Aug 6;15(1):20220986. doi: 10.1515/tnsci-2022-0986. eCollection 2024 Jan 1. Transl Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39118828 Free PMC article.
Abstract
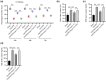
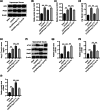
Background: Death among resuscitated patients is mainly caused by brain injury after cardiac arrest/cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CA/CPR). The angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2)/angiotensin (Ang)-(1-7)/Mas receptor (MasR) axis has beneficial effects on brain injury. Therefore, we examined the roles of the ACE2/Ang-(1-7)/MasR axis in brain injury after CA/CPR.
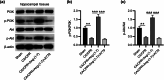
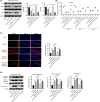
Method: We used a total of 76 male New Zealand rabbits, among which 10 rabbits underwent sham operation and 66 rabbits received CA/CPR. Neurological functions were determined by assessing serum levels of neuron-specific enolase and S100 calcium-binding protein B and neurological deficit scores. Brain water content was estimated. Neuronal apoptosis in the hippocampus was assessed by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling assays. The expression levels of various genes were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and western blotting.
Results: Ang-(1-7) (MasR activator) alleviated CA/CPR-induced neurological deficits, brain edema, and neuronal damage, and A779 (MasR antagonist) had the opposite functions. The stimulation of ACE2/Ang-(1-7)/MasR inactivated the ACE/Ang II/AT1R axis and activated PI3K/Akt signaling. Inhibiting PI3K/Akt signaling inhibited Ang-(1-7)-mediated protection against brain damage after CA/CPR.
Conclusion: Collectively, the ACE2/Ang-(1-7)/MasR axis alleviates CA/CPR-induced brain injury through attenuating hippocampal neuronal apoptosis by activating PI3K/Akt signaling.
Keywords: ACE2/Ang-(1-7)/MasR axis; PI3K/Akt; apoptosis; brain injury; cardiac arrest; cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Activation of Angiotensin-converting Enzyme 2 Protects Against Lipopolysaccharide-induced Glial Activation by Modulating Angiotensin-converting Enzyme 2/Angiotensin (1-7)/Mas Receptor Axis.Mol Neurobiol. 2023 Jan;60(1):203-227. doi: 10.1007/s12035-022-03061-5. Epub 2022 Oct 17. Mol Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 36251234
-
Stimulation of ACE2/ANG(1-7)/Mas Axis by Diminazene Ameliorates Alzheimer's Disease in the D-Galactose-Ovariectomized Rat Model: Role of PI3K/Akt Pathway.Mol Neurobiol. 2018 Oct;55(10):8188-8202. doi: 10.1007/s12035-018-0966-3. Epub 2018 Mar 7. Mol Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 29516284
-
The angiotensin converting enzyme 2/angiotensin-(1-7)/Mas Receptor axis as a key player in alveolar bone remodeling.Bone. 2019 Nov;128:115041. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2019.115041. Epub 2019 Aug 20. Bone. 2019. PMID: 31442676
-
The ACE2/Ang (1-7)/MasR axis as an emerging target for antihypertensive peptides.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2021;61(15):2572-2586. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2020.1781049. Epub 2020 Jun 18. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2021. PMID: 32551837 Review.
-
Angiotensin converting enzyme 2: a new important player in the regulation of glycemia.IUBMB Life. 2013 Sep;65(9):731-8. doi: 10.1002/iub.1190. Epub 2013 Jul 29. IUBMB Life. 2013. PMID: 23893738 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sanfilippo F, Murabito P, Messina A, Dezio V, Busalacchi D, Ristagno G, et al. Cerebral regional oxygen saturation during cardiopulmonary resuscitation and return of spontaneous circulation: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Resuscitation. 2021;159:19–27. - PubMed
-
- Fischer M, Böttiger BW, Popov-Cenic S, Hossmann KA. Thrombolysis using plasminogen activator and heparin reduces cerebral no-reflow after resuscitation from cardiac arrest: an experimental study in the cat. Intensive Care Med. 1996;22(11):1214–23. - PubMed
-
- Lin SR, O'Connor MJ, Fischer HW, King A. The effect of combined dextran and streptokinase on cerebral function and blood flow after cardiac arrest: and experimental study on the dog. Invest Radiol. 1978;13(6):490–8. - PubMed
-
- Madl C, Kramer L, Domanovits H, Woolard RH, Gervais H, Gendo A, et al. Improved outcome prediction in unconscious cardiac arrest survivors with sensory evoked potentials compared with clinical assessment. Crit Care Med. 2000;28(3):721–6. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
