Label-Free Electrochemical Detection of DNA Hybridization: A Method for COVID-19 Diagnosis
- PMID: 38624377
- PMCID: PMC7247285
- DOI: 10.1007/s41403-020-00103-z
Label-Free Electrochemical Detection of DNA Hybridization: A Method for COVID-19 Diagnosis
Abstract
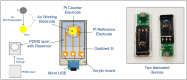
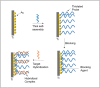
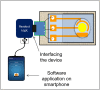
This paper presents label-free electrochemical transduction as a suitable scheme for COVID-19-specific viral RNA/c-DNA detection, with an aim to facilitate point of care diagnosis. In lieu of this, we discuss the proposed electrochemical biosensing scheme, based on electrodeposited gold nanoparticles as the transducing elements. Specific to this approach, here, the protocols associated with the immobilization of the single-stranded probe nucleotide on to the biosensor, have also been laid out. This paper also discusses the methods of electrochemical analysis, to be used for data acquisition and subsequent calibration, in relation to target analyte detection. Towards facilitating portable diagnosis, development of miniaturized sensors and their integration with readout units have also been discussed.
Keywords: COVID-19; Electrochemical Sensors; Miniaturization.
© Indian National Academy of Engineering 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThere is no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Akhavan O, Ghaderi E, Rahighi R (2012) Toward single-DNA electrochemical biosensing by graphene nanowalls. ACS Nano 6(4):2904–2916 - PubMed
-
- Bakker E, Telting-Diaz M (2002) Electrochemical sensors. Anal Chem 74(12):2781–2800 - PubMed
-
- Boon EM, Ceres DM, Drummond TG, Hill MG, Barton JK (2000) Mutation detection by electrocatalysis at DNA-modified electrodes. Nat Biotechnol 18(10):1096–1100 - PubMed
-
- Drummond TG, Hill MG, Barton JK (2003) Electrochemical DNA sensors. Nat Biotechnol 21(10):1192 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
