COVID-19 susceptibility: potential of ACE2 polymorphisms
- PMID: 38624559
- PMCID: PMC7502288
- DOI: 10.1186/s43042-020-00099-9
COVID-19 susceptibility: potential of ACE2 polymorphisms
Abstract
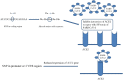
Background: Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) is a metallopeptidase that primarily functions as a negative regulator of renin angiotensin system (RAS) by converting angiotensin II (Ang II) to angiotensin 1-7. Contrary to this, another RAS component, angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) catalyzes synthesis of Ang II from angiotensin I (Ang I) that functions as active compound in blood pressure regulation. This indicates importance of ACE/ACE2 level in regulating blood pressure by targeting Ang II. An outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) highlighted the additional role of ACE2 as a receptor for SARS coronavirus (SARS-CoV) infection.
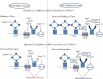
Main body of the abstract: ACE2 is a functional receptor for SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2. Activation of spike (S)-protein by either type II transmembrane serine proteases (TTSPs) or cathepsin-mediated cleavage initiates receptor binding and viral entry. In addition to TTSPs, ACE2 can also be trimmed by ADAM 17 (a disintegrin and metalloproteinase 17) that competes for the same receptor. Cleavage by TTSPs activates ACE2 receptor for binding, whereas ADAM17 releases extracellular fragment called soluble ACE2 (sACE2). Structural studies of both ACE2 and S-protein have found critical sites involved in binding mechanism. In addition to studies on structural motifs, few single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNPs) studies have been done to find an association between genetic variants and SARS susceptibility. Though no association was found in those reports, but seeing the non-reproducibility of SNP studies among different ethnic groups, screening of ACE2 SNPs in individual population can be undertaken.
Short conclusion: Thus, screening for novel SNPs focussing on recently identified critical regions of ACE2 can be targeted to monitor susceptibility towards coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).
Keywords: ACE2; COVID-19; Coronavirus; SARS-CoV-2; Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS); Single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP).
© The Author(s) 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsNo competing interests
Figures

References
-
- Skeggs LT, Dorer FE, Levine M, Lentz KE, Kahn JR (1980) The biochemistry of the renin-angiotensin system. Adv Exp Med Biol 130:1–27 - PubMed
-
- Lavoie JL, Sigmund CD (2003) Minireview: overview of the renin-angiotensin system-an endocrine and paracrine system. Endocrinology 144(6):2179–2183 - PubMed
-
- Dinh DT, Frauman AG, Johnston CI, Fabiani ME (2001) Angiotensin receptors: distribution, signalling and function. Clin Sci 100(5):481–492 - PubMed
-
- Donoghue M, Hsieh F, Baronas E, Godbout K, Gosselin M, Stagliano N et al (2000) A novel angiotensin converting enzyme related corboxypeptidase (ACE2) converts angiotensin I to angiotensin 1-9. Circ Res 87:E1–E9 - PubMed
-
- Tipnis SR, Hooper NM, Hyde R, Karran E, Christie G, Turner AJ (2000) A human homolog of angiotensin converting enzyme. Cloning and functional expression as a captopril-insensitive carboxypeptidase. J Biol Chem 275(43):33238–33243 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
