Unconventional monetary policies in an agent-based model with mark-to-market standards
- PMID: 38624912
- PMCID: PMC8965549
- DOI: 10.1007/s43253-022-00065-8
Unconventional monetary policies in an agent-based model with mark-to-market standards
Abstract
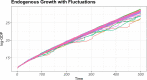
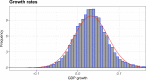
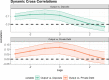
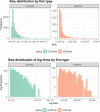
We employ an agent-based model to shed light on the macroeconomic effects of accounting principles, unconventional monetary policies, and of their possible interactions. If mark-to-market accounting standards may entail positive feedbacks which amplify economic or financial shocks, unconventional policies may introduce negative feedbacks that might dampen instabilities in financial and real markets. For these reasons, we jointly study these two sets of policies by employing a modified version of the Schumpeter meeting Keynes (K+S) macroeconomic agent-based model. Our results confirm that, due to its pro-cyclical nature, the mark-to-market accounting standard amplifies credit cycles, generating more instability with respect to a simulated economy wherein the historical accounting principle is employed. In contrast, unconventional monetary policy is counter-cyclical and it improves macroeconomic indicators. Finally, we study a scenario wherein mark-to-market accounting and unconventional monetary policy interact. We find that unconventional monetary policy can counterbalance the negative effects brought about by the application of mark-to-market accounting. Our results suggest that unconventional monetary policy instruments should not be considered as temporary interventions to be employed only during crisis periods. They should be part of the toolbox of central banks also in normal times.
Keywords: Accounting principles; Agent-based models; Mark-to-market; Unconventional monetary policy.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to European Association for Evolutionary Political Economy and EAEPE Academy GmbH 2022.
Figures





References
-
- Adrian T, Shin HS (2010) Liquidity and leverage. J Financ Intermed 19(3):418–437
-
- Altavilla C, Giannone D (2017) The effectiveness of non-standard monetary policy measures: evidence from survey data. J Appl Econ 32(5):952–964
-
- Arslan Y, Drehmann M, Hofmann B et al (2020) Central bank bond purchases in emerging market economies. BIS Bulletin 20, Bank for International Settlements
-
- Ashraf Q, Gershman B, Howitt P (2016) How inflation affects macroeconomic performance: an agent-based computational investigation. Macroecon Dyn 20(2):558–581
-
- Assenza T, Cardaci A, Delli Gatti D, Grazzini J (2017) Policy experiments in an agent-based model with credit networks. Economics - The Open-Access. Open-Assessment E-Journal, 66
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
