Prognostic Effect of Masked Morning Hypertension in Chinese Inpatients With Non-dialysis Chronic Kidney Disease: A Multicenter Retrospective Study
- PMID: 38625716
- PMCID: PMC11247133
- DOI: 10.1093/ajh/hpae044
Prognostic Effect of Masked Morning Hypertension in Chinese Inpatients With Non-dialysis Chronic Kidney Disease: A Multicenter Retrospective Study
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to elucidate the prognostic role of Masked Morning Hypertension (MMH) in non-dialysis-dependent chronic kidney disease (NDD-CKD).
Methods: 2,130 NDD-CKD patients of the inpatient department were categorized into four blood pressure (BP) groups: clinical normotension (CH-), clinical hypertension (CH+) with morning hypertension (MH+), and without MH+ (MH-) respectively. The correlation between these four BP types and the primary (all-cause mortality) and secondary endpoints (cardio-cerebrovascular disease [CVD] and end-stage kidney disease [ESKD]) was analyzed.
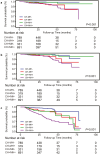
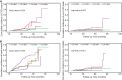
Results: The prevalence of MH and MMH were 47.4% and 14.98%, respectively. Morning hypertension independently increased the risk of all-cause mortality (P = 0.004) and CVD (P < 0.001) but not ESKD (P = 0.092). Masked morning hypertension was associated with heightened all-cause mortality (HR = 4.22, 95% CI = 1.31-13.59; P = 0.02) and CVD events (HR = 5.14, 95% CI = 1.37-19.23; P = 0.02), with no significant association with ESKD (HR = 1.18, 95% CI = 0.65-2.15; P = 0.60). When considering non-CVD deaths as a competing risk factor, a high cumulative incidence of CVD events was observed in the MMH group (HR = 5.16, 95% CI = 1.39-19.08).
Conclusions: MMH is an independent risk factor for all-cause mortality and combined cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events in NDD-CKD patients, underscoring its prognostic significance. This highlights the need for comprehensive management of MH in this population.
Keywords: all-cause mortality; blood pressure; cardio-cerebrovascular disease; chronic kidney disease; end-stage kidney disease; hypertension; masked morning hypertension.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of American Journal of Hypertension, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prognostic value of morning blood pressure surge in chronic kidney disease.J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2024 Oct;26(10):1155-1162. doi: 10.1111/jch.14885. Epub 2024 Aug 19. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2024. PMID: 39161159 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Effect of Isolated Nocturnal Hypertension in Chinese Patients With Nondialysis Chronic Kidney Disease.J Am Heart Assoc. 2016 Oct 10;5(10):e004198. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.116.004198. J Am Heart Assoc. 2016. PMID: 27792646 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Significance of Ambulatory BP Monitoring in CKD: A Report from the Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort (CRIC) Study.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020 Nov;31(11):2609-2621. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2020030236. Epub 2020 Sep 24. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 32973085 Free PMC article.
-
Masked Hypertension in CKD: Increased Prevalence and Risk for Cardiovascular and Renal Events.Curr Cardiol Rep. 2019 May 20;21(7):58. doi: 10.1007/s11886-019-1154-4. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2019. PMID: 31111326 Review.
-
Masked phenomenon: renal and cardiovascular complications; review and updates.Blood Press. 2024 Dec;33(1):2383234. doi: 10.1080/08037051.2024.2383234. Epub 2024 Jul 26. Blood Press. 2024. PMID: 39056371 Review.
References
-
- Ishikawa J, Kario K, Eguchi K, Morinari M, Hoshide S, Ishikawa S, Shimada K; J-MORE Group. Regular alcohol drinking is a determinant of masked morning hypertension detected by home blood pressure monitoring in medicated hypertensive patients with well-controlled clinic blood pressure: the Jichi Morning Hypertension Research (J-MORE) study. Hypertens Res 2006; 29:679–686. - PubMed
-
- Umemura S, Arima H, Arima S, Asayama K, Dohi Y, Hirooka Y, Horio T, Hoshide S, Ikeda S, Ishimitsu T, Ito M, Ito S, Iwashima Y, Kai H, Kamide K, Kanno Y, Kashihara N, Kawano Y, Kikuchi T, Kitamura K, Kitazono T, Kohara K, Kudo M, Kumagai H, Matsumura K, Matsuura H, Miura K, Mukoyama M, Nakamura S, Ohkubo T, Ohya Y, Okura T, Rakugi H, Saitoh S, Shibata H, Shimosawa T, Suzuki H, Takahashi S, Tamura K, Tomiyama H, Tsuchihashi T, Ueda S, Uehara Y, Urata H, Hirawa N.. The Japanese Society of Hypertension Guidelines for the management of hypertension (JSH 2019). Hypertens Res 2019; 42:1235–1481. - PubMed
-
- Li X, Lian R, Zhu Y, Ke J, Li M, Wang C, Lou T.. Masked morning hypertension correlated with target organ damage in non-dialysis patients with chronic kidney disease. J Hypertens 2020; 38:1794–1801. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

