Irisin alleviates obesity-induced bone loss by inhibiting interleukin 6 expression via TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB axis in adipocytes
- PMID: 38626873
- PMCID: PMC11954833
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jare.2024.04.013
Irisin alleviates obesity-induced bone loss by inhibiting interleukin 6 expression via TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB axis in adipocytes
Abstract
Introduction: Obesity-induced bone loss affects the life quality of patients all over the world. Irisin, one of the myokines, plays an essential role in bone and fat metabolism.
Objective: Investigate the effects of irisin on bone metabolism via adipocytes in the bone marrow microenvironment.
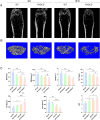
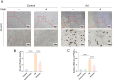
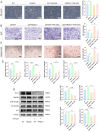
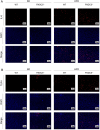
Methods: In this study, we fed fibronectin type III domain-containing protein 5 (FNDC5, the precursor protein of irisin) knockout mice (FNDC5-/-) with a high-fat diet (HFD) for 10 weeks. The quality of bone mass was assessed by micro-CT analysis, histological staining, and dynamic bone formation. In vitro, the lipogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) was assayed by Oil Red O staining, and the osteogenic differentiation was assayed by alkaline phosphatase staining. Meanwhile, the gene expression in the BMSC-differentiated adipocytes by RNA sequence and the involved pathway of irisin were determined by western blot and qRT-PCR were performed.
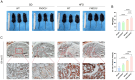
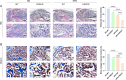
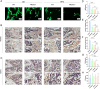
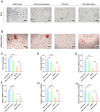
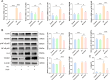
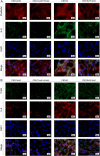
Results: The FNDC5-/- mice fed with a HFD showed an increased body weight, fat content of the bone marrow and bone, and a decreased bone formation compared with those with a standard diet (SD). In vitro, irisin inhibited the differentiation of BMSCs into adipocytes and alleviated the inhibition of osteogenesis derived from BMSCs by the adipocyte supernatant. RNA sequence and blocking experiment showed that irisin reduced the production of interleukin 6 (IL-6) in adipocytes through downregulating the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway. Immunofluorescence staining of bone marrow further confirmed an increased IL-6 expression in the FNDC5-/- mice fed with HFD compared with those fed with SD, which suffered serious bone loss.
Conclusion: Irisin downregulates activation of the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway, thereby reducing IL-6 production in adipocytes to enhance the osteogenesis of BMSCs. Thus, the rescue of osteogenesis of BMSCs, initially inhibited by IL-6, is a potential therapeutic target to mitigate obesity-induced osteoporosis.
Keywords: Adipocytes; IL-6; Irisin; Osteogenesis; TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB.
Copyright © 2023. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Finkelstein E.A., Khavjou O.A., Thompson H., Trogdon J.G., Pan L., Sherry B., et al. Obesity and severe obesity forecasts through 2030. Am J Prev Med. 2012;42(6):563–570. - PubMed
-
- Kelly T., Yang W., Chen C.S., Reynolds K., He J. Global burden of obesity in 2005 and projections to 2030. Int J Obes (Lond) 2008;32(9):1431–1437. - PubMed
-
- Wang Y.C., McPherson K., Marsh T., Gortmaker S.L., Brown M. Health and economic burden of the projected obesity trends in the USA and the UK. Lancet. 2011;378(9793):815–825. - PubMed
-
- Piche M.E., Tchernof A., Despres J.P. Obesity phenotypes, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. Circ Res. 2020;126(11):1477–1500. - PubMed
-
- Hannan M.T., Felson D.T., Anderson J.J. Bone mineral density in elderly men and women: results from the Framingham osteoporosis study. J Bone Miner Res Off J Am Soc Bone Miner Res. 1992;7(5):547–553. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

