Antioxidant, antidiabetic effects and polyphenolic contents of propolis from Siirt, Turkey
- PMID: 38628175
- PMCID: PMC11016413
- DOI: 10.1002/fsn3.3958
Antioxidant, antidiabetic effects and polyphenolic contents of propolis from Siirt, Turkey
Abstract
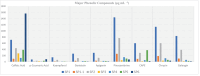
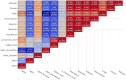
Propolis, a natural product collected by honeybees from various plant sources, has gained significant attention due to its diverse bioactive compounds and potential therapeutic properties. To further explore its contents and biological activities, this study aimed to analyze the phenolic compounds in Siirt propolis extracts obtained using different solvents, namely ethanol, water, and ethanol-water mixtures. The primary objective of this research was to investigate the phenolic profile, as well as the antidiabetic and antioxidant activities of the propolis extracts. Chemical profiling of extracts was performed using LC-MS/MS. The antioxidant potential of the propolis extracts was evaluated through free radical scavenging methods, including DPPH and ABTS assays. As a result of these analyses, propolis extracts showed moderate radical scavenging potential with 13.86%-35.72% for DPPH and 33.62%-62.50% for ABTS at a concentration of 30 μg mL-1, respectively. This radical scavenging potential of the extracts sheds light on its ability to combat oxidative stress, which is implicated in the development of diabetes, and its potential effects on cellular health. Additionally, the study assessed the antidiabetic properties of the propolis extracts by examining their inhibition effects on α-amylase and α-glycosidase enzymes. Extracts with high phenolic content showed a high inhibitory effect against α-glucosidase with an IC50 of 5.72 ± 0.83 μg mL-1. This research provided significant findings regarding the potential use of propolis in the treatment of diabetes and related metabolic disorders.
Keywords: Propolis; antioxidant activity; radical scavenging; α‐amylase; α‐glycosidase.
© 2024 The Authors. Food Science & Nutrition published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comprehensive Metabolite Profiling of Berdav Propolis Using LC-MS/MS: Determination of Antioxidant, Anticholinergic, Antiglaucoma, and Antidiabetic Effects.Molecules. 2023 Feb 11;28(4):1739. doi: 10.3390/molecules28041739. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36838726 Free PMC article.
-
Screening of Antiglaucoma, Antidiabetic, Anti-Alzheimer, and Antioxidant Activities of Astragalus alopecurus Pall-Analysis of Phenolics Profiles by LC-MS/MS.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Apr 28;16(5):659. doi: 10.3390/ph16050659. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37242442 Free PMC article.
-
LC/MS/MS Phenolic Profile, Antioxidant Capacity, Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) and Glutathione S Transferase (GST) Inhibitory Properties of Ultrasound-Assisted Propolis Extracts.Chem Biodivers. 2023 Apr;20(4):e202300049. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.202300049. Epub 2023 Mar 27. Chem Biodivers. 2023. PMID: 36866854
-
Propolis Stands out as a Multifaceted Natural Product: Meta-Analysis on Its Sources, Bioactivities, Applications, and Future Perspectives.Life (Basel). 2025 May 9;15(5):764. doi: 10.3390/life15050764. Life (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40430191 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential Role of Propolis in the Prevention and Treatment of Metabolic Diseases.Plants (Basel). 2021 Apr 27;10(5):883. doi: 10.3390/plants10050883. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33925692 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Design, Synthesis, Biological Evaluation, and Molecular Docking Studies of Novel 1,3,4-Thiadiazole Derivatives Targeting Both Aldose Reductase and α-Glucosidase for Diabetes Mellitus.ACS Omega. 2025 May 5;10(18):18812-18828. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.5c00566. eCollection 2025 May 13. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 40385215 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alencar, S. M. , Oldoni, T. L. C. , Castro, M. L. , Cabral, I. S. R. , Costa‐Neto, C. M. , Cury, J. A. , Rosalen, P. L. , & Ikegaki, M. (2007). Chemical composition and biological activity of a new type of Brazilian propolis: Red propolis. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 113(2), 278–283. - PubMed
-
- Andrade, J. K. S. , Denadai, M. , de Oliveira, C. S. , Nunes, M. L. , & Narain, N. (2017). Evaluation of bioactive compounds potential and antioxidant activity of brown, green and red propolis from Brazilian northeast region. Food Research International, 101, 129–138. - PubMed
-
- Blois, M. S. (1958). Antioxidant determinations by the use of a stable free radical. Nature, 181, 1199–1200. 10.1038/1811199a0 - DOI
-
- Çelemli, G. Ö. , Özkırım, A. , & Arı, H. Ü. (2011). Bal Arılarından Gelen Sağlık Propolis. Bilim Teknik Dergisi, 526, 28–30.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

