A lipid/PLGA nanocomplex to reshape tumor immune microenvironment for colon cancer therapy
- PMID: 38628547
- PMCID: PMC11018539
- DOI: 10.1093/rb/rbae036
A lipid/PLGA nanocomplex to reshape tumor immune microenvironment for colon cancer therapy
Abstract
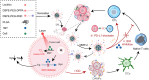
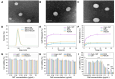
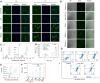
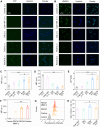
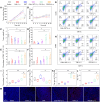
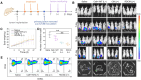
Immune checkpoint blockade therapy provides a new strategy for tumor treatment; however, the insufficient infiltration of cytotoxic T cells and immunosuppression in tumor microenvironment lead to unsatisfied effects. Herein, we reported a lipid/PLGA nanocomplex (RDCM) co-loaded with the photosensitizer Ce6 and the indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) inhibitor 1MT to improve immunotherapy of colon cancer. Arginine-glycine-aspartic acid (RGD) as the targeting moiety was conjugated on 1,2-distearoyl-snglycero-3-phosphoethanolamine lipid via polyethylene glycol (PEG), and programmed cell death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) peptide inhibitor DPPA (sequence: CPLGVRGK-GGG-d(NYSKPTDRQYHF)) was immobilized on the terminal group of PEG via matrix metalloproteinase 2 sensitive peptide linker. The Ce6 and 1MT were encapsulated in PLGA nanoparticles. The drug loaded nanoparticles were composited with RGD and DPPA modified lipid and lecithin to form lipid/PLGA nanocomplexes. When the nanocomplexes were delivered to tumor, DPPA was released by the cleavage of a matrix metalloproteinase 2-sensitive peptide linker for PD-L1 binding. RGD facilitated the cellular internalization of nanocomplexes via avβ3 integrin. Strong immunogenic cell death was induced by 1O2 generated from Ce6 irradiation under 660 nm laser. 1MT inhibited the activity of IDO and reduced the inhibition of cytotoxic T cells caused by kynurenine accumulation in the tumor microenvironment. The RDCM facilitated the maturation of dendritic cells, inhibited the activity of IDO, and markedly recruited the proportion of tumor-infiltrating cytotoxic T cells in CT26 tumor-bearing mice, triggering a robust immunological memory effect, thus effectively preventing tumor metastasis. The results indicated that the RDCM with dual IDO and PD-L1 inhibition effects is a promising platform for targeted photoimmunotherapy of colon cancer.
Keywords: IDO inhibition; colon cancer; immune checkpoint blockade; lipid/PLGA nanocomplex; photodynamic therapy.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Co-Delivery of Doxorubicin and Anti-PD-L1 Peptide in Lipid/PLGA Nanocomplexes for the Chemo-Immunotherapy of Cancer.Mol Pharm. 2022 Sep 5;19(9):3439-3449. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.2c00611. Epub 2022 Aug 22. Mol Pharm. 2022. PMID: 35994700
-
Multi-shell structured upconversion nanocarriers that combine IDO inhibitor-induced immunotherapy with NIR-triggered photodynamic therapy for deep tumors.Biomater Sci. 2023 Jun 27;11(13):4684-4699. doi: 10.1039/d3bm00248a. Biomater Sci. 2023. PMID: 37219321
-
Peptide vaccine-conjugated mesoporous carriers synergize with immunogenic cell death and PD-L1 blockade for amplified immunotherapy of metastatic spinal.J Nanobiotechnology. 2021 Aug 12;19(1):243. doi: 10.1186/s12951-021-00975-5. J Nanobiotechnology. 2021. PMID: 34384429 Free PMC article.
-
Light-responsive hyaluronic acid nanomicelles co-loaded with an IDO inhibitor focus targeted photoimmunotherapy against "immune cold" cancer.Biomater Sci. 2021 Nov 23;9(23):8019-8031. doi: 10.1039/d1bm01409a. Biomater Sci. 2021. PMID: 34718362
-
Epigenetic strategies synergize with PD-L1/PD-1 targeted cancer immunotherapies to enhance antitumor responses.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2020 May;10(5):723-733. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2019.09.006. Epub 2019 Sep 25. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2020. PMID: 32528824 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nano drug delivery systems for advanced immune checkpoint blockade therapy.Theranostics. 2025 Apr 13;15(11):5440-5480. doi: 10.7150/thno.112475. eCollection 2025. Theranostics. 2025. PMID: 40303342 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Near-infrared photoimmunotherapy: mechanisms, applications, and future perspectives in cancer research.Antib Ther. 2025 Jan 20;8(1):68-85. doi: 10.1093/abt/tbaf001. eCollection 2025 Jan. Antib Ther. 2025. PMID: 39958565 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The micro(nano)plastics perspective: exploring cancer development and therapy.Mol Cancer. 2025 Jan 24;24(1):30. doi: 10.1186/s12943-025-02230-z. Mol Cancer. 2025. PMID: 39856719 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanomaterials based on hollow gold nanospheres for cancer therapy.Regen Biomater. 2024 Oct 24;11:rbae126. doi: 10.1093/rb/rbae126. eCollection 2024. Regen Biomater. 2024. PMID: 39664940 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The prognostic value of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in colorectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Gastroenterol. 2025 Aug 20;25(1):603. doi: 10.1186/s12876-025-04124-2. BMC Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40836217 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hu L, Cao Z, Ma L, Liu Z, Liao G, Wang J, Shen S, Li D, Yang X.. The potentiated checkpoint blockade immunotherapy by ROS-responsive nanocarrier-mediated cascade chemo-photodynamic therapy. Biomaterials 2019;223:119469. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

