A Systematic Review of the Application of Artificial Intelligence in Nursing Care: Where are We, and What's Next?
- PMID: 38628616
- PMCID: PMC11020344
- DOI: 10.2147/JMDH.S459946
A Systematic Review of the Application of Artificial Intelligence in Nursing Care: Where are We, and What's Next?
Abstract
Background: Integrating Artificial Intelligence (AI) into healthcare has transformed the landscape of patient care and healthcare delivery. Despite this, there remains a notable gap in the existing literature synthesizing the comprehensive understanding of AI's utilization in nursing care.
Objective: This systematic review aims to synthesize the available evidence to comprehensively understand the application of AI in nursing care.
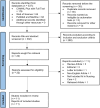
Methods: Studies published between January 2019 and December 2023, identified through CINAHL Plus with Full Text, Web of Science, PubMed, and Medline, were included in this review. The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses guidelines guided the identification, screening, exclusion, and inclusion of articles. The convergent integrated analysis framework, as proposed by the Joanna Briggs Institute, was employed to synthesize data from the included studies for theme generation.
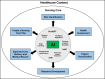
Results: A total of 337 records were identified from databases. Among them, 35 duplicates were removed, and 302 records underwent eligibility screening. After applying inclusion and exclusion criteria, eleven studies were deemed eligible and included in this review. Through data synthesis of these studies, six themes pertaining to the use of AI in nursing care were identified: 1) Risk Identification, 2) Health Assessment, 3) Patient Classification, 4) Research Development, 5) Improved Care Delivery and Medical Records, and 6) Developing a Nursing Care Plan.
Conclusion: This systematic review contributes valuable insights into the multifaceted applications of AI in nursing care. Through the synthesis of data from the included studies, six distinct themes emerged. These findings not only consolidate the current knowledge base but also underscore the diverse ways in which AI is shaping and improving nursing care practices.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; nursing care; patient care; systematic review.
© 2024 Ruksakulpiwat et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Deng J, Lin Y. The benefits and challenges of ChatGPT: an overview. Front Comput Intell Sys. 2022;2(2):81–83.
-
- Wu J, Shang S. Managing uncertainty in AI-enabled decision making and achieving sustainability. Sustainability. 2020;12(21):8758.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

