Traditional Chinese medicine in osteoporosis: from pathogenesis to potential activity
- PMID: 38628648
- PMCID: PMC11019011
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1370900
Traditional Chinese medicine in osteoporosis: from pathogenesis to potential activity
Abstract
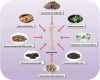
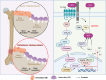
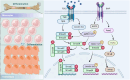
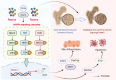
Osteoporosis characterized by decreased bone density and mass, is a systemic bone disease with the destruction of microstructure and increase in fragility. Osteoporosis is attributed to multiple causes, including aging, inflammation, diabetes mellitus, and other factors induced by the adverse effects of medications. Without treatment, osteoporosis will further progress and bring great trouble to human life. Due to the various causes, the treatment of osteoporosis is mainly aimed at improving bone metabolism, inhibiting bone resorption, and promoting bone formation. Although the currently approved drugs can reduce the risk of fragility fractures in individuals, a single drug has limitations in terms of safety and effectiveness. By contrast, traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), a characteristic discipline in China, including syndrome differentiation, Chinese medicine prescription, and active ingredients, shows unique advantages in the treatment of osteoporosis and has received attention all over the world. Therefore, this review summarized the pathogenic factors, pathogenesis, therapy limitations, and advantages of TCM, aiming at providing new ideas for the prevention and treatment of OP.
Keywords: osteoporosis; pathogenesis; pathogenic factors; traditional Chinese medicine; treatment.
Copyright © 2024 Cao, Hu, Ning, Dou, Ding, Wang, Wang, Sang, Yang, Shi, Hao and Han.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Andreoli A., Bazzocchi A., Celi M., Lauro D., Sorge R., Tarantino U., et al. (2011). Relationship between body composition, body mass index and bone mineral density in a large population of normal, osteopenic and osteoporotic women. Radiol. Med. 116, 1115–1123. 10.1007/s11547-011-0689-2 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ayers C., Kansagara D., Lazur B., Fu R., Kwon A., Harrod C. (2023). Effectiveness and safety of treatments to prevent fractures in people with low bone mass or primary osteoporosis: a living systematic review and network meta-analysis for the American college of physicians. Ann. Intern Med. 176, 182–195. 10.7326/M22-0684 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

