Long-Term Outcomes of Endovascular Aneurysm Repair in Patients Aged ≤70 Years
- PMID: 38628930
- PMCID: PMC11018108
- DOI: 10.3400/avd.oa.23-00072
Long-Term Outcomes of Endovascular Aneurysm Repair in Patients Aged ≤70 Years
Abstract
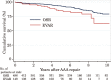
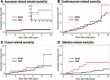
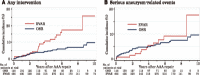
Objectives: The efficacy of endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR) against abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) in younger patients remains unknown. Hence, the current study aimed to investigate whether the aneurysm-related mortality rate of EVAR is acceptable among patients aged ≤70 years. Methods: Among 644 patients, 148 underwent EVAR (EVAR group), and 496 received open surgical repair (OSR group). The cumulative incidence rates of aneurysm-related death, any intervention, and serious aneurysm-related events after AAA repair were evaluated using the cumulative incidence function in the presence of competing risks. Results: The EVAR group had higher prevalences of several comorbidities, and overall survival for the EVAR group was significantly inferior to that of the OSR group. The cumulative incidence rates of aneurysm-related death, any intervention, and serious aneurysm-related events at 5 years were 1.5%, 11.7%, and 6.4% in the EVAR group and 1.3%, 5.3%, and 5.9% in the OSR group, respectively. EVAR was not a significant prognostic factor of aneurysm-related mortality and serious aneurysm-related events. However, it was an independent poor prognostic factor of any intervention. Conclusion: EVAR was not a significant prognostic factor of aneurysm-related mortality and serious aneurysm-related events. Therefore, it demonstrated acceptable procedure-related long-term outcomes, at least in high-risk young patients.
Keywords: abdominal aortic aneurysm; endovascular aneurysm repair; open surgical repair; young patients.
@ 2024 The Editorial Committee of Annals of Vascular Diseases.
Figures
References
-
- Patel R, Sweeting MJ, Powell JT, et al. Endovascular versus open repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm in 15-years’ follow-up of the UK endovascular aneurysm repair trial 1 (EVAR trial 1): a randomized controlled trial. Lancet 2016; 388: 2366–74. - PubMed
-
- van Schaik TG, Yeung KK, Verhagen HJ, et al. Long-term survival and secondar procedures after open or endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysms. J Vasc Surg 2017; 66: 1379–89. - PubMed
-
- Lederle FA, Kyriakides TC, Stroupe KT, et al. Open versus endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm. N Engl J Med 2019; 380: 2126–35. - PubMed
-
- Lederle FA, Freischlag JA, Kyriakides TC, et al. Long-term comparison of endovascular and open repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm. N Engl J Med 2012; 367: 1988–97. - PubMed

