PLD2 deletion ameliorates sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy by suppressing cardiomyocyte pyroptosis via the NLRP3/caspase 1/GSDMD pathway
- PMID: 38630134
- PMCID: PMC11106193
- DOI: 10.1007/s00011-024-01881-w
PLD2 deletion ameliorates sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy by suppressing cardiomyocyte pyroptosis via the NLRP3/caspase 1/GSDMD pathway
Abstract
Objective: Sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy (SICM) is a life-threatening complication. Phospholipase D2 (PLD2) is crucial in mediating inflammatory reactions and is associated with the prognosis of patients with sepsis. Whether PLD2 is involved in the pathophysiology of SICM remains unknown. This study aimed to investigate the effect of PLD2 knockout on SICM and to explore potential mechanisms.
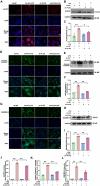
Methods: The SICM model was established using cecal ligation and puncture in wild-type and PLD2-knockout mice and lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced H9C2 cardiomyocytes. Transfection with PLD2-shRNA lentivirus and a PLD2 overexpression plasmid were used to interfere with PLD2 expression in H9C2 cells. Cardiac pathological alterations, cardiac function, markers of myocardial injury, and inflammatory factors were used to evaluate the SICM model. The expression of pyroptosis-related proteins (NLRP3, cleaved caspase 1, and GSDMD-N) was assessed using western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry.
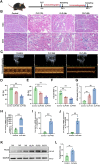
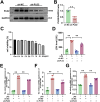
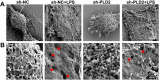
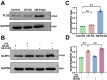
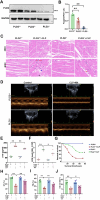
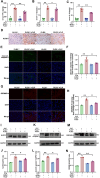
Results: SICM mice had myocardial tissue damage, increased inflammatory response, and impaired heart function, accompanied by elevated PLD2 expression. PLD2 deletion improved cardiac histological changes, mitigated cTNI production, and enhanced the survival of the SICM mice. Compared with controls, PLD2-knockdown H9C2 exhibits a decrease in inflammatory markers and lactate dehydrogenase production, and scanning electron microscopy results suggest that pyroptosis may be involved. The overexpression of PLD2 increased the expression of NLRP3 in cardiomyocytes. In addition, PLD2 deletion decreased the expression of pyroptosis-related proteins in SICM mice and LPS-induced H9C2 cells.
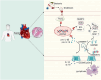
Conclusion: PLD2 deletion is involved in SICM pathogenesis and is associated with the inhibition of the myocardial inflammatory response and pyroptosis through the NLRP3/caspase 1/GSDMD pathway.
Keywords: Caspase 1; GSDMD; NLRP3; Phospholipase D2; Pyroptosis; Sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors assert that they do not own any conflicting interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

