Evaluation of the mechanism of Gong Ying San activity on dairy cows mastitis by network pharmacology and metabolomics analysis
- PMID: 38630770
- PMCID: PMC11023200
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0299234
Evaluation of the mechanism of Gong Ying San activity on dairy cows mastitis by network pharmacology and metabolomics analysis
Abstract
Objectives: The goal of this investigation was to identify the main compounds and the pharmacological mechanism of the traditional Chinese medicine formulation, Gong Ying San (GYS), by infrared spectral absorption characteristics, metabolomics, network pharmacology, and molecular-docking analysis for mastitis. The antibacterial and antioxidant activities were determined in vitro.
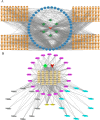
Methods: The chemical constituents of GYS were detected by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography Q-extractive mass spectrometry (UHPLC-QE-MS). Related compounds were screened from the Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology Database and Analysis Platform (TCMSP, http://tcmspw.com/tcmsp.php) and the Encyclopedia of Traditional Chinese Medicine (ETCM, http://www.tcmip.cn/ETCM/index.php/Home/) databases; genes associated with mastitis were identified in DisGENT. A protein-protein interaction (PPI) network was generated using STRING. Gene ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment screening was conducted using the R module. Molecular-docking analyses were performed with the AutoDockTools V1.5.6.
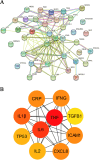
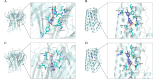
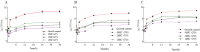
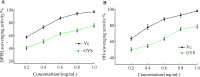
Results: Fifty-four possible compounds in GYS with forty likely targets were found. The compound-target-network analysis showed that five of the ingredients, quercetin, luteolin, kaempferol, beta-sitosterol, and stigmasterol, had degree values >41.6, and the genes TNF, IL-6, IL-1β, ICAM1, CXCL8, CRP, IFNG, TP53, IL-2, and TGFB1 were core targets in the network. Enrichment analysis revealed that pathways associated with cancer, lipids, atherosclerosis, and PI3K-Akt signaling pathways may be critical in the pharmacology network. Molecular-docking data supported the hypothesis that quercetin and luteolin interacted well with TNF-α and IL-6.
Conclusions: An integrative investigation based on a bioinformatics-network topology provided new insights into the synergistic, multicomponent mechanisms of GYS's anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and antioxidant activities. It revealed novel possibilities for developing new combination medications for reducing mastitis and its complications.
Copyright: © 2024 Gao et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Potential Molecular Mechanisms of Ephedra Herb in the Treatment of Nephrotic Syndrome Based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Jul 5;2022:9214589. doi: 10.1155/2022/9214589. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35837376 Free PMC article.
-
Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking and Experimental Verification Revealing the Mechanism of Fule Cream against Childhood Atopic Dermatitis.Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2024;20(6):860-875. doi: 10.2174/0115734099257922230925074407. Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2024. PMID: 37807411
-
Study the Mechanism of Gualou Niubang Decoction in Treating Plasma Cell Mastitis Based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Jun 15;2022:5780936. doi: 10.1155/2022/5780936. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35757473 Free PMC article.
-
Researching the molecular mechanisms of Taohong Siwu Decoction in the treatment of varicocele-associated male infertility using network pharmacology and molecular docking: A review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Aug 4;102(31):e34476. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000034476. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37543801 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploration of the mechanism of Zisheng Shenqi decoction against gout arthritis using network pharmacology.Comput Biol Chem. 2021 Feb;90:107358. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2020.107358. Epub 2020 Aug 8. Comput Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33243703 Review.
Cited by
-
Bioactive Compounds and Probiotics Mitigate Mastitis by Targeting NF-κB Signaling Pathway.Biomolecules. 2024 Aug 15;14(8):1011. doi: 10.3390/biom14081011. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39199398 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrated multi-omics analysis reveals that Gongying San ameliorates subclinical mastitis by modulating intestinal microbiota and metabolites in dairy cows.Front Vet Sci. 2025 Jun 9;12:1589900. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1589900. eCollection 2025. Front Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40552082 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mao J. Detection of main pathogenic bacteria of cow mastitis based on PCR technique[J].The Chinese Livestock and Poultry Breeding. 2023;19(10):170–174.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

