NTRK-rearranged spindle cell neoplasm: Initial observation of imaging appearance and clinicopathologic correlation
- PMID: 38631176
- PMCID: PMC11586688
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clinimag.2024.110134
NTRK-rearranged spindle cell neoplasm: Initial observation of imaging appearance and clinicopathologic correlation
Abstract
Objective: To explore pre-treatment imaging findings of neurotrophic tyrosine receptor kinase (NTRK)-rearranged spindle cell neoplasm, an emerging group of molecularly defined soft tissue tumors and summarize the clinical course, including TRK inhibitor therapy response.
Materials and methods: This retrospective study included 8 women and 4 men with NTRK-rearranged spindle cell neoplasm (median age, 35.5 years, range, 0-66). Available pre-treatment MRI, CT, PET, and US imaging were reviewed. Tumor histology and the patients' clinical course were reviewed.
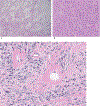
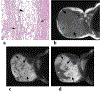
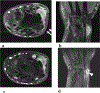
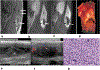
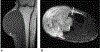
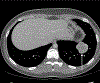
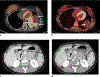
Results: Primary tumors were located within the soft tissue, lungs, kidney, and breast with soft tissue being the most prevalent site (n = 6). Pre-treatment MRI (n = 4) revealed linear hypointense signal foci and contrast enhancement in all patients with hemorrhage in half of the tumors. A tail sign (n = 1) and fluid levels (n = 1) were less frequent. Ultrasound showed well-marginated hypoechoic masses with internal flow. Primary tumors were all non-calcified on CT (4/4). Metastases were FDG-avid (4/4). Among the 8 patients who developed metastasis, 7 developed pulmonary metastases. All four patients who received NTRK inhibitor therapy showed an initial decrease in tumor size or FDG uptake.
Conclusion: NTRK-rearranged neoplasms may occur as enhancing masses with linear hypointense signal foci on MRI and FDG avid metastases on PET. Pulmonary metastases were frequent in our study. Initial treatment response is observed in most patients.
Keywords: CT; Imaging; MR; NTRK; PET; Soft tissue sarcoma; Ultrasound.
Copyright © 2024 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest None.
Figures
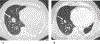
References
-
- Eggert A, Grotzer MA, Ikegaki N, Liu XG, Evans AE, Brodeur GM. Expression of the neurotrophin receptor TrkA down-regulates expression and function of angiogenic stimulators in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. Cancer Res. 2002; 62(6):1802–1808. - PubMed
-
- Lagadec C, Meignan S, Adriaenssens E, Foveau B, Vanhecke E, Romon R, et al. TrkA overexpression enhances growth and metastasis of breast cancer cells. Oncogene. 2009; 28(18):1960–1970. - PubMed
-
- Vaishnavi A, Le AT, Doebele RC. TRKing down an old oncogene in a new era of targeted therapy. Cancer Discov. 2015;5(1):25–34. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-14-0765 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- International Agency for Research on Cancer WHO, International Academy of Pathology. WHO classification of tumours of soft tissue and bone tumours: International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), 2020: 287.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

