Predicting early recurrence after resection of initially unresectable colorectal liver metastases: the role of baseline and pre-surgery clinical, radiological and molecular factors in a real-life multicentre experience
- PMID: 38631269
- PMCID: PMC11027482
- DOI: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2024.102991
Predicting early recurrence after resection of initially unresectable colorectal liver metastases: the role of baseline and pre-surgery clinical, radiological and molecular factors in a real-life multicentre experience
Abstract
Background: Advances in surgical techniques and systemic treatments have increased the likelihood of achieving radical surgery and long-term survival in metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) patients with initially unresectable colorectal liver metastases (CRLMs). Nonetheless, roughly half of the patients resected after an upfront systemic therapy experience disease relapse within 6 months from surgery, thus leading to the question whether surgery is actually beneficial for these patients.
Materials and methods: A real-world dataset of mCRC patients with initially unresectable liver-limited disease treated with conversion chemotherapy followed by radical resection of CRLMs at three high-volume Italian institutions was retrospectively assessed with the aim of investigating the association of baseline and pre-surgical clinical, radiological and molecular factors with the risk of relapse within 6 or 12 months from surgery.
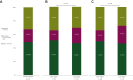
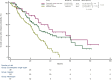
Results: Overall, 268 patients were included in the analysis and 207 (77%) experienced recurrence. Ninety-six (46%) of them had disease relapse within 6 months after CRLM resection and in spite of several variables associated with early recurrence at univariate analyses, only primary tumour resection at diagnosis [odds ratio (OR) 0.53, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.32-0.89, P = 0.02] remained significant in the multivariable model. Among patients with resected primary tumours, pN+ stage was associated with higher risk of disease relapse within 6 months (OR 3.02, 95% CI 1.23-7.41, P = 0.02). One hundred and forty-nine patients (72%) had disease relapse within 12 months after CRLMs resection but none of the analysed variables was independently associated with outcome.
Conclusions: Clinical, radiological and molecular factors assessed before and after conversion chemotherapy do not reliably predict early recurrence after secondary resection of initially unresectable CRLMs. While novel markers are needed to optimize the cost/efficacy balance of surgical procedures, CRLM resection should be offered as soon as metastases become resectable during first-line chemotherapy to all patients eligible for surgery.
Keywords: conversion chemotherapy; early disease recurrence; secondary resection; unresectable colorectal liver metastases.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rescue surgery for unresectable colorectal liver metastases downstaged by chemotherapy: a model to predict long-term survival.Ann Surg. 2004 Oct;240(4):644-57; discussion 657-8. doi: 10.1097/01.sla.0000141198.92114.f6. Ann Surg. 2004. PMID: 15383792 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical efficacy of liver resection after downsizing systemic chemotherapy for initially unresectable liver metastases.World J Surg Oncol. 2016 Feb 25;14:56. doi: 10.1186/s12957-016-0807-7. World J Surg Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26911142 Free PMC article.
-
Liver resection for primarily unresectable colorectal metastases downsized by chemotherapy.J Gastrointest Surg. 2007 Mar;11(3):318-24. doi: 10.1007/s11605-006-0070-2. J Gastrointest Surg. 2007. PMID: 17458605
-
[Diagnosis and treatment of colorectal liver metastases - workflow].Zentralbl Chir. 2008 Jun;133(3):267-84. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1076796. Zentralbl Chir. 2008. PMID: 18563694 Review. German.
-
Conversion strategies with chemotherapy plus targeted agents for colorectal cancer liver-only metastases: A systematic review.Eur J Cancer. 2020 Dec;141:225-238. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2020.09.037. Epub 2020 Nov 12. Eur J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 33189037
Cited by
-
Translating efficacy of liver transplantation in liver-limited metastatic colorectal cancer into clinical practice: the TransMet trial.ESMO Open. 2024 Sep;9(9):103669. doi: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2024.103669. Epub 2024 Aug 20. ESMO Open. 2024. PMID: 39341646 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cervantes A., Adam R., Roselló S., et al. Metastatic colorectal cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2023;34:10–32. - PubMed
-
- Bolhuis K., Kos M., van Oijen M.G.H., et al. Conversion strategies with chemotherapy plus targeted agents for colorectal cancer liver-only metastases: a systematic review. Eur J Cancer. 2020;141:225–238. - PubMed
-
- Folprecht G., Gruenberger T., Bechstein W., et al. Survival of patients with initially unresectable colorectal liver metastases treated with FOLFOX/cetuximab or FOLFIRI/cetuximab in a multidisciplinary concept (CELIM study)†. Ann Oncol. 2014;25:1018–1025. - PubMed
-
- Dhir M., Sasson A.R. Surgical management of liver metastases from colorectal cancer. J Oncol Pract. 2016;12:33–39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

