The circadian rhythm: A new target of natural products that can protect against diseases of the metabolic system, cardiovascular system, and nervous system
- PMID: 38631431
- PMCID: PMC11954810
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jare.2024.04.005
The circadian rhythm: A new target of natural products that can protect against diseases of the metabolic system, cardiovascular system, and nervous system
Abstract
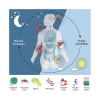
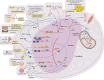
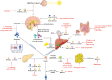
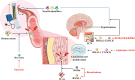
Background: The treatment of metabolic system, cardiovascular system, and nervous system diseases remains to be explored. In the internal environment of organisms, the metabolism of substances such as carbohydrates, lipids and proteins (including biohormones and enzymes) exhibit a certain circadian rhythm to maintain the energy supply and material cycle needed for the normal activities of organisms. As a key factor for the health of organisms, the circadian rhythm can be disrupted by pathological conditions, and this disruption accelerates the progression of diseases and results in a vicious cycle. The current treatments targeting the circadian rhythm for the treatment of metabolic system, cardiovascular system, and nervous system diseases have certain limitations, and the identification of safer and more effective circadian rhythm regulators is needed.
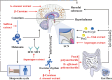
Aim of the review: To systematically assess the possibility of using the biological clock as a natural product target for disease intervention, this work reviews a range of evidence on the potential effectiveness of natural products targeting the circadian rhythm to protect against diseases of the metabolic system, cardiovascular system, and nervous system. This manuscript focuses on how natural products restore normal function by affecting the amplitude of the expression of circadian factors, sleep/wake cycles and the structure of the gut microbiota.
Key scientific concepts of the review: This work proposes that the circadian rhythm, which is regulated by the amplitude of the expression of circadian rhythm-related factors and the sleep/wake cycle, is crucial for diseases of the metabolic system, cardiovascular system and nervous system and is a new target for slowing the progression of diseases through the use of natural products. This manuscript provides a reference for the molecular modeling of natural products that target the circadian rhythm and provides a new perspective for the time-targeted action of drugs.
Keywords: Cardiovascular system; Circadian rhythm; Metabolic system; Natural products; Nervous system.
Copyright © 2024. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interaction between Tea Polyphenols and Intestinal Microbiota in Host Metabolic Diseases from the Perspective of the Gut-Brain Axis.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2020 Jul;64(14):e2000187. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.202000187. Epub 2020 Jun 21. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2020. PMID: 32506625 Review.
-
Circadian rhythm as a therapeutic target.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2021 Apr;20(4):287-307. doi: 10.1038/s41573-020-00109-w. Epub 2021 Feb 15. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2021. PMID: 33589815 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Diet and Exercise on Circadian Rhythm: Role of Gut Microbiota in Immune and Metabolic Systems.Nutrients. 2023 Jun 14;15(12):2743. doi: 10.3390/nu15122743. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37375647 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acute Sleep-Wake Cycle Shift Results in Community Alteration of Human Gut Microbiome.mSphere. 2020 Feb 12;5(1):e00914-19. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00914-19. mSphere. 2020. PMID: 32051239 Free PMC article.
-
Circadian rhythm, sleep pattern, and metabolic consequences: an overview on cardiovascular risk factors.Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig. 2014 Apr;18(1):47-52. doi: 10.1515/hmbci-2013-0057. Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig. 2014. PMID: 25390000 Review.
Cited by
-
Design and implementation of a radiomic-driven intelligent dental hospital diversion system utilizing multilabel imaging data.J Transl Med. 2024 Dec 20;22(1):1123. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05958-2. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39707394 Free PMC article.
-
Natural Compounds for Preventing Age-Related Diseases and Cancers.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 9;25(14):7530. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147530. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39062777 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

