B cells and the coordination of immune checkpoint inhibitor response in patients with solid tumors
- PMID: 38631710
- PMCID: PMC11029261
- DOI: 10.1136/jitc-2023-008636
B cells and the coordination of immune checkpoint inhibitor response in patients with solid tumors
Abstract
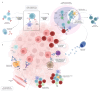
Immunotherapy profoundly changed the landscape of cancer therapy by providing long-lasting responses in subsets of patients and is now the standard of care in several solid tumor types. However, immunotherapy activity beyond conventional immune checkpoint inhibition is plateauing, and biomarkers are overall lacking to guide treatment selection. Most studies have focused on T cell engagement and response, but there is a growing evidence that B cells may be key players in the establishment of an organized immune response, notably through tertiary lymphoid structures. Mechanisms of B cell response include antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity and phagocytosis, promotion of CD4+ and CD8+ T cell activation, maintenance of antitumor immune memory. In several solid tumor types, higher levels of B cells, specific B cell subpopulations, or the presence of tertiary lymphoid structures have been associated with improved outcomes on immune checkpoint inhibitors. The fate of B cell subpopulations may be widely influenced by the cytokine milieu, with versatile roles for B-specific cytokines B cell activating factor and B cell attracting chemokine-1/CXCL13, and a master regulatory role for IL-10. Roles of B cell-specific immune checkpoints such as TIM-1 are emerging and could represent potential therapeutic targets. Overall, the expanding field of B cells in solid tumors of holds promise for the improvement of current immunotherapy strategies and patient selection.
Keywords: B cell; Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors; Tumor microenvironment - TME.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: RF. Honoraria: Bayer, Astellas, Janssen, BMS, MSD, Ipsen, Pfizer, Merck, Astra Zeneca. MT. NoneMR-C. NoneLC-A. NoneLR. NoneNN. Honoraria: Merck, PfizerJ-MJ. NoneLB. NoneMN. NoneBE. Honoraria: Bristol:Myers Squibb, Ipsen, Oncorena, Pfizer. Consulting or Advisory Role : AVEO, Bristol:Myers Squibb, Ipsen, Oncorena, Pfizer. Research Funding : BMS France (Inst). Travel, Accommodations, Expenses : Bristol:Myers Squibb, Ipsen, MSDLC. NoneLA. Consulting or Advisory Role: Astellas Pharma (Inst), Bristol:Myers Squibb (Inst), Eisai (Inst), Ipsen (Inst), Janssen (Inst), MSD (Inst), Pfizer (Inst), Roche (Inst). Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: BMS, Ipsen, MSDNC. Scientific grants from Sanofi, BMS, Cytune Pharma, Scientist advisory board from Servier, lectures for AstraZeneca.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Systemic treatments for metastatic cutaneous melanoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 6;2(2):CD011123. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011123.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29405038 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between tumor mutation burden and the tumor microenvironment predicts the prognosis of pan-cancer anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy.Front Immunol. 2025 Jul 24;16:1557461. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1557461. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40777041 Free PMC article.
-
Oncolytic reovirus enhances the effect of CEA immunotherapy when combined with PD1-PDL1 inhibitor in a colorectal cancer model.Immunotherapy. 2025 Apr;17(6):425-435. doi: 10.1080/1750743X.2025.2501926. Epub 2025 May 12. Immunotherapy. 2025. PMID: 40353308
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Short-Term Memory Impairment.2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31424720 Free Books & Documents.
Cited by
-
Construction of hot tumor classification models in gastrointestinal cancers.J Transl Med. 2025 Feb 21;23(1):218. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06230-x. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 39984938 Free PMC article.
-
Immune checkpoint inhibitor-related myasthenia gravis, myocarditis and myositis: further insights.Support Care Cancer. 2025 Jun 2;33(6):528. doi: 10.1007/s00520-025-09602-7. Support Care Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40455120 No abstract available.
-
Subtype- and race-specific variations in the immune landscape of breast cancer: therapeutic implications.NPJ Breast Cancer. 2025 Jul 24;11(1):78. doi: 10.1038/s41523-025-00799-8. NPJ Breast Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40707500 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer Vaccines: Recent Insights and Future Directions.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 19;25(20):11256. doi: 10.3390/ijms252011256. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39457036 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mature tertiary lymphoid structures evoke intra-tumoral T and B cell responses via progenitor exhausted CD4+ T cells in head and neck cancer.Nat Commun. 2025 May 7;16(1):4228. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-59341-w. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40335494 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Busch VI. Verhandlungen Ärztlicher Gesellschaften. Berliner Klin Wochenschrift 1866;245–6.
-
- Bumpus HC. The apparent disappearance of pulmonary metastasis in a case of hypernephroma following nephrectomy1. J Urol 1928;20:185–92. 10.1016/S0022-5347(17)73147-3 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
