Temporal trends in lifetime risks of atrial fibrillation and its complications between 2000 and 2022: Danish, nationwide, population based cohort study
- PMID: 38631726
- PMCID: PMC11019491
- DOI: 10.1136/bmj-2023-077209
Temporal trends in lifetime risks of atrial fibrillation and its complications between 2000 and 2022: Danish, nationwide, population based cohort study
Abstract
Objectives: To examine how the lifetime risks of atrial fibrillation and of complications after atrial fibrillation changed over time.
Design: Danish, nationwide, population based cohort study.
Setting: Population of Denmark from 1 January 2000 to 31 December 2022.
Participants: 3.5 million individuals (51.7% women and 48.3% men) who did not have atrial fibrillation at 45 years of age or older were followed up until incident atrial fibrillation, migration, death, or end of follow-up, whichever came first. All 362 721 individuals with incident atrial fibrillation (46.4% women and 53.6% men), but with no prevalent complication, were further followed up until incident heart failure, stroke, or myocardial infarction.
Main outcome measures: Lifetime risk of atrial fibrillation and lifetime risks of complications after atrial fibrillation over two prespecified periods (2000-10 v 2011-22).
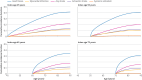
Results: The lifetime risk of atrial fibrillation increased from 24.2% in 2000-10 to 30.9% in 2011-22 (difference 6.7% (95% confidence interval 6.5% to 6.8%)). After atrial fibrillation, the most frequent complication was heart failure with a lifetime risk of 42.9% in 2000-10 and 42.1% in 2011-22 (-0.8% (-3.8% to 2.2%)). Individuals with atrial fibrillation lost 14.4 years with no heart failure. The lifetime risks of stroke and of myocardial infarction after atrial fibrillation decreased slightly between the two periods, from 22.4% to 19.9% for stroke (-2.5% (-4.2% to -0.7%)) and from 13.7% to 9.8% for myocardial infarction (-3.9% (-5.3% to -2.4%). No evidence was reported of a differential decrease between men and women.
Conclusion: Lifetime risk of atrial fibrillation increased over two decades of follow-up. In individuals with atrial fibrillation, about two in five developed heart failure and one in five had a stroke over their remaining lifetime after atrial fibrillation diagnosis, with no or only small improvement over time. Stroke risks and heart failure prevention strategies are needed for people with atrial fibrillation.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2019. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form at www.icmje.org/disclosure-of-interest and declare NV has served as an advisory board member and consultant for AstraZeneca, no fees were received personally. SPJ has an institutional research grant from BMS/Pfizer (not related to the current study) and personal consulting fees received from BMS and Pfizer. EJB has a grant R01HL092577; American Heart Association AF AHA_18SFRN34110082. LF is supported by the Health Research Foundation of Central Denmark Region and has served as a consultant for BMS/Pfizer and AstraZeneca. LT was supported by a research grant from the American Heart Association (18SFRN34150007). PC and LS declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Dai H, Zhang Q, Much AA, et al. . Global, regional, and national prevalence, incidence, mortality, and risk factors for atrial fibrillation, 1990-2017: results from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Eur Heart J Qual Care Clin Outcomes 2021;7:574-82. 10.1093/ehjqcco/qcaa061. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical