[Comparison of effectiveness of three surgical methods in treatment of Pauwels type Ⅲ femoral neck fracture in young and middle-aged patients]
- PMID: 38632059
- PMCID: PMC11024523
- DOI: 10.7507/1002-1892.202401110
[Comparison of effectiveness of three surgical methods in treatment of Pauwels type Ⅲ femoral neck fracture in young and middle-aged patients]
Abstract
Objective: To compare the effectiveness of three surgical methods in the treatment of Pauwels type Ⅲ femoral neck fracture in young and middle-aged patients, in order to provide reference for clinical selection of appropriate surgical methods.
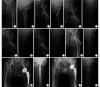
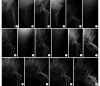
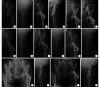
Methods: The clinical data of 103 patients with Pauwels type Ⅲ femoral neck fracture who met the selection criteria between June 2018 and December 2021 were retrospectively analyzed. The fractures were fixed with hollow screws in an inverted triangular shape (37 cases, hollow screw group), hollow screws in an inverted triangular shape combined with eccentric shaft screw (34 cases, eccentric shaft screw group), and hollow screws in an inverted triangular shape combined with medial support plate (32 cases, support plate group). There was no significant difference in age, gender, cause of injury, body mass index, time from injury to operation, side of the fracture, and Garden classification, whether they were in traction preoperatively, and other baseline data between groups ( P>0.05). The operation time, intraoperative blood loss, the number of fluoroscopy, the length of hospital stay, early postoperative complication and postoperative weight-bearing time of the three groups were recorded. Harris score was used to evaluate joint function at 6 and 12 months after operation, and the difference between the two time points (change value) was calculated for comparison between groups. X-ray films were reviewed to evaluate the quality of fracture reduction (Garden index) and healing, as well as the occurrence of internal fixation failure and femoral head necrosis.
Results: The patients of the three groups were successfully completed. Compared with the hollow screw group and the eccentric shaft screw group, the operation time and intraoperative blood loss of the support plate group significantly increased, the number of fluoroscopy reduced, and the quality of fracture reduction was better, the differences were significant ( P<0.05). The operation time, intraoperative blood loss, and the number of fluoroscopy of the hollow screw group were less than those of the eccentric shaft screw group, the differences were significant ( P<0.05). There was no significant difference in the length of hospital stay between groups ( P>0.05). All patients in the three groups were followed up 21-52 months, with an average follow-up time of 36.0 months, and there was no significant difference between groups ( P>0.05). The incisions of all patients healed by first intention. Imaging reexamination showed that there was no significant difference in the incidence of fracture nonunion between groups ( P>0.05). The fracture healing, partial weight-bearing, and full weight-bearing were significantly earlier in the eccentric shaft screw group and the support plate group than in the hollow screw group ( P<0.05). There was no significant difference in change value of Harris score, the incidence of postoperative deep venous thrombosis and femoral head necrosis between groups ( P>0.05); however, the incidence of internal fixation failure in the support plate group and the eccentric shaft screw group was significantly lower than that in the hollow screw group ( P<0.05). The incidence of postoperative lateral thigh irritation in the support plate group was significantly lower than that in the hollow screw group ( P<0.05); there was no significant difference between the eccentric shaft screw group and the other two groups ( P>0.05). The overall incidences of postoperative complications in the eccentric shaft screw group and the support plate group were significantly lower than that in the hollow screw group ( P<0.05).
Conclusion: For young and middle-aged patients with Pauwels type Ⅲ femoral neck fracture, compared with simple hollow screw fixation in an inverted triangular shape, combined with medial support plate or eccentric shaft screw internal fixation can shorten the fracture healing time, reduce the incidences of postoperative complication, more conducive to early functional exercise of the affected limb; at the same time, the operation time and blood loss of combined eccentric shaft screw internal fixation are less than those of combined medial support plate internal fixation, so the hollow screw in an inverted triangular shape combined with eccentric shaft screw fixation may be a better choice.
目的: 比较 3 种手术方式治疗中青年 Pauwels Ⅲ型股骨颈骨折的疗效,以期为临床选择恰当术式提供参考。.
方法: 回顾性分析 2018 年6月—2021年12月收治且符合选择标准的 103 例 Pauwels Ⅲ型股骨颈骨折患者临床资料。采用倒三角空心螺钉固定 37 例(空心螺钉组)、倒三角空心螺钉联合偏轴螺钉固定 34 例(偏轴螺钉组)、倒三角空心螺钉联合内侧支撑钢板固定 32 例(支撑钢板组)。3 组患者年龄、性别、致伤原因、身体质量指数、受伤至手术时间、骨折侧别及 Garden 分型、术前是否牵引等基线资料比较,差异均无统计学意义( P>0.05)。记录 3组手术时间、术中出血量、术中透视次数、住院时间、早期并发症发生情况、术后开始负重时间;术后 6、12 个月 Harris 评分评价关节功能,计算两时间点差值(变化值)进行组间比较;复查 X 线片,评价骨折复位质量(Garden 指数)及愈合情况,以及内固定失效、股骨头坏死发生情况。.
结果: 3 组手术均顺利完成。与空心螺钉组及偏轴螺钉组相比,支撑钢板组手术时间及术中出血量均增多、透视次数减少、骨折复位质量更好,差异均有统计学意义( P<0.05);空心螺钉组与偏轴螺钉组骨折复位质量差异无统计学意义( P>0.05),但手术时间、术中出血量及透视次数均少于偏轴螺钉组( P<0.05)。3 组住院时间差异均无统计学意义( P>0.05)。术后 3 组患者均获随访,随访时间 21~52 个月,平均 36.0 个月,随访时间组间差异无统计学意义( P>0.05)。患者切口均Ⅰ期愈合。影像学复查示,3 组骨折不愈合发生率差异无统计学意义( P>0.05);偏轴螺钉组及支撑钢板组骨折愈合以及患者术后开始部分负重、完全负重均早于空心螺钉组( P<0.05),偏轴螺钉组与支撑钢板组上述指标差异均无统计学意义( P>0.05)。3 组术后 Harris 评分变化值及下肢深静脉血栓形成、股骨头坏死发生率比较,差异均无统计学意义( P>0.05);但支撑钢板组及偏轴螺钉组内固定失效发生率低于空心螺钉组( P<0.05),而偏轴螺钉组与支撑钢板组间差异无统计学意义( P>0.05)。支撑钢板组大腿外侧激惹症状发生率低于空心螺钉组( P<0.05),其余组间比较差异无统计学意义( P>0.05)。偏轴螺钉组及支撑钢板组术后并发症总体发生率均低于空心螺钉组( P<0.05),而偏轴螺钉组与支撑钢板组间差异无统计学意义( P>0.05)。.
结论: 对于中青年 Pauwels Ⅲ型股骨颈骨折,与单纯倒三角空心螺钉内固定相比,联合内侧支撑钢板或偏轴螺钉内固定可缩短骨折愈合时间、降低术后并发症发生率,更有利于患肢早期功能锻炼。同时,联合偏轴螺钉内固定手术时间及出血量少于联合内侧支撑钢板内固定,因此倒三角空心螺钉联合偏轴螺钉固定可能是更好选择。.
Keywords: Pauwels type Ⅲ femoral neck fracture; eccentric shaft screw; hollow screw; internal fixation; medial support plate.
Conflict of interest statement
利益冲突 在课题研究和文章撰写过程中不存在利益冲突;经费支持没有影响文章观点和对研究数据客观结果的统计分析及其报道
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Effectiveness of guide plate with mortise-tenon joint structure combined with off-axis fixation in treatment of Pauwels type Ⅲ femoral neck fractures].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2025 Mar 15;39(3):284-289. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.202411083. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 40101902 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
[Effectiveness analysis of biplanar vertical fixation and inverted triangle fixation with hollow screw for Pauwels type Ⅲ femoral neck fracture in young and middle-aged patients].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2024 Aug 15;38(8):961-967. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.202404070. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 39175318 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
[Comparison of femoral neck system and inverted triangle cannulated screws fixations in treatment of Pauwels typle Ⅲ femoral neck fractures].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2021 Sep 15;35(9):1111-1118. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.202102046. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34523275 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Medial femoral plate with cannulated screw for Pauwels type III femoral neck fracture: A meta-analysis.J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2021;34(2):169-177. doi: 10.3233/BMR-200183. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2021. PMID: 33164925 Review.
-
Computer-assisted cannulated screw internal fixation versus conventional cannulated screw internal fixation for femoral neck fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Orthop Surg Res. 2021 Nov 22;16(1):687. doi: 10.1186/s13018-021-02806-7. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021. PMID: 34809649 Free PMC article.
References
-
- 韩哲, 曹东东, 孙翔, 等 中青年PauwelsⅢ型股骨颈骨折治疗的研究进展. 中国中西医结合外科杂志. 2023;29(5):716–719.
-
- 冀家琛, 陈豪杰, 杨博, 等 股骨颈动力交叉钉系统内固定治疗股骨颈骨折术后早期股骨头坏死的危险因素分析. 中国修复重建外科杂志. 2023;37(2):162–167.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
