Distinct growth patterns in seedling and tillering wheat plants suggests a developmentally restricted role of HYD2 in salt-stress response
- PMID: 38632145
- PMCID: PMC11024023
- DOI: 10.1007/s00299-024-03206-x
Distinct growth patterns in seedling and tillering wheat plants suggests a developmentally restricted role of HYD2 in salt-stress response
Abstract
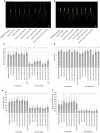
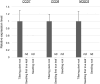
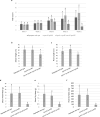
Mutants lacking functional HYD2 homoeologs showed improved seedling growth, but comparable or increased susceptibility to salt stress in tillering plants, suggesting a developmentally restricted role of HYD2 in salt response. Salinity stress threatens global food security by reducing the yield of staple crops such as wheat (Triticum ssp.). Understanding how wheat responds to salinity stress is crucial for developing climate resilient varieties. In this study, we examined the interplay between carotenoid metabolism and the response to salt (NaCl) stress, a specific form of salinity stress, in tetraploid wheat plants with mutations in carotenoid β-hydroxylase 1 (HYD1) and HYD2. Our investigation encompassed both the vulnerable seedling stage and the more developed tillering stage of wheat plant growth. Mutant combinations lacking functional HYD2 homoeologs, including hyd-A2 hyd-B2, hyd-A1 hyd-A2 hyd-B2, hyd-B1 hyd-A2 hyd-B2, and hyd-A1 hyd-B1 hyd-A2 hyd-B2, had longer first true leaves and slightly enhanced root growth during germination under salt stress compared to the segregate wild-type (control) plants. Interestingly, these mutant seedlings also showed decreased levels of neoxanthin and violaxanthin (xanthophylls derived from β-carotene) and an increase in β-carotene in roots. However, tillering hyd mutant and segregate wild-type plants generally did not differ in their height, tiller count, and biomass production under acute or prolonged salt stress, except for decreases in these parameters observed in the hyd-A1 hyd-B1 hyd-A2 hyd-B2 mutant that indicate its heightened susceptibility to salt stress. Taken together, these findings suggest a significant, yet developmentally restricted role of HYD2 homoeologs in salt-stress response in tetraploid wheat. They also show that hyd-A2 hyd-B2 mutant plants, previously demonstrated for possessing enriched nutritional (β-carotene) content, maintain an unimpaired ability to withstand salt stress.
Keywords: Carotenoid; Carotenoid β-hydroxylase (HYD); Hydroxylation; Salinity; Salt-stress response; Wheat; Xanthophyll; β-Carotene.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mutant combinations of lycopene ɛ-cyclase and β-carotene hydroxylase 2 homoeologs increased β-carotene accumulation in endosperm of tetraploid wheat (Triticum turgidum L.) grains.Plant Biotechnol J. 2022 Mar;20(3):564-576. doi: 10.1111/pbi.13738. Epub 2021 Nov 18. Plant Biotechnol J. 2022. PMID: 34695292 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic dissection of the roles of β-hydroxylases in carotenoid metabolism, photosynthesis, and plant growth in tetraploid wheat (Triticum turgidum L.).Theor Appl Genet. 2023 Jan;136(1):8. doi: 10.1007/s00122-023-04276-3. Epub 2023 Jan 19. Theor Appl Genet. 2023. PMID: 36656368 Free PMC article.
-
Cloning and comparative analysis of carotenoid β-hydroxylase genes provides new insights into carotenoid metabolism in tetraploid (Triticum turgidum ssp. durum) and hexaploid (Triticum aestivum) wheat grains.Plant Mol Biol. 2012 Dec;80(6):631-46. doi: 10.1007/s11103-012-9972-4. Epub 2012 Sep 27. Plant Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 23015203 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into Salinity Tolerance in Wheat.Genes (Basel). 2024 Apr 29;15(5):573. doi: 10.3390/genes15050573. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38790202 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic Basis of Tillering Angle from Other Plants to Wheat: Current Progress and Future Perspectives.Plants (Basel). 2024 Nov 18;13(22):3237. doi: 10.3390/plants13223237. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39599446 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptomic and metabolomic analysis reveals the molecular mechanism of exogenous melatonin improves salt tolerance in eggplants.Front Plant Sci. 2025 Jan 10;15:1523582. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1523582. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2025. PMID: 39866315 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abramoff M, Magalhães P, Ram S (2004) Image processing with ImageJ. Biophotonics Int 11:36–42
-
- Applied Biosystems (2008) Guide to performing relative quantitation of gene expression using Real-Time quantitative PCR
-
- Choulet F, Alberti A, Theil S, Glover N, Barbe V, Daron J, Pingault L, Sourdille P, Couloux A, Paux E, Leroy P, Mangenot S, Guilhot N, Le Gouis J, Balfourier F, Alaux M, Jamilloux V, Poulain J, Durand C, Bellec A, Gaspin C, Safar J, Dolezel J, Rogers J, Vandepoele K, Aury J-M, Mayer K, Berges H, Quesneville H, Wincker P, Feuillet C. Structural and functional partitioning of bread wheat chromosome 3B. Science. 2014;345:1249721. doi: 10.1126/science.1249721. - DOI - PubMed

