tRNA modification reprogramming contributes to artemisinin resistance in Plasmodium falciparum
- PMID: 38632343
- PMCID: PMC11153160
- DOI: 10.1038/s41564-024-01664-3
tRNA modification reprogramming contributes to artemisinin resistance in Plasmodium falciparum
Abstract
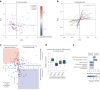
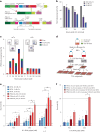
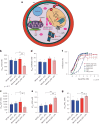
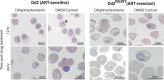
Plasmodium falciparum artemisinin (ART) resistance is driven by mutations in kelch-like protein 13 (PfK13). Quiescence, a key aspect of resistance, may also be regulated by a yet unidentified epigenetic pathway. Transfer RNA modification reprogramming and codon bias translation is a conserved epitranscriptomic translational control mechanism that allows cells to rapidly respond to stress. We report a role for this mechanism in ART-resistant parasites by combining tRNA modification, proteomic and codon usage analyses in ring-stage ART-sensitive and ART-resistant parasites in response to drug. Post-drug, ART-resistant parasites differentially hypomodify mcm5s2U on tRNA and possess a subset of proteins, including PfK13, that are regulated by Lys codon-biased translation. Conditional knockdown of the terminal s2U thiouridylase, PfMnmA, in an ART-sensitive parasite background led to increased ART survival, suggesting that hypomodification can alter the parasite ART response. This study describes an epitranscriptomic pathway via tRNA s2U reprogramming that ART-resistant parasites may employ to survive ART-induced stress.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests
Figures








Similar articles
-
Role of Plasmodium falciparum Kelch 13 Protein Mutations in P. falciparum Populations from Northeastern Myanmar in Mediating Artemisinin Resistance.mBio. 2020 Feb 25;11(1):e01134-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01134-19. mBio. 2020. PMID: 32098812 Free PMC article.
-
Ring stage dormancy of Plasmodium falciparum tolerant to artemisinin and its analogues - A genetically regulated "Sleeping Beauty".Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist. 2023 Apr;21:61-64. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpddr.2023.01.002. Epub 2023 Jan 16. Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist. 2023. PMID: 36708651 Free PMC article.
-
Plasmodium falciparum artemisinin resistance: something gained in translation.Trends Parasitol. 2024 Jul;40(7):541-543. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2024.06.004. Epub 2024 Jun 22. Trends Parasitol. 2024. PMID: 38910099
-
The many paths to artemisinin resistance in Plasmodium falciparum.Trends Parasitol. 2023 Dec;39(12):1060-1073. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2023.09.011. Epub 2023 Oct 11. Trends Parasitol. 2023. PMID: 37833166 Review.
-
Plasmodium falciparum: multifaceted resistance to artemisinins.Malar J. 2016 Mar 9;15:149. doi: 10.1186/s12936-016-1206-9. Malar J. 2016. PMID: 26955948 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
In Vivo Engineered CAR-T Cell Therapy: Lessons Built from COVID-19 mRNA Vaccines.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 28;26(7):3119. doi: 10.3390/ijms26073119. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40243757 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Malaria: past, present, and future.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025 Jun 17;10(1):188. doi: 10.1038/s41392-025-02246-3. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025. PMID: 40523953 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Charting new territory: The Plasmodium falciparum tRNA modification landscape.Biomed J. 2025 Apr;48(2):100745. doi: 10.1016/j.bj.2024.100745. Epub 2024 May 9. Biomed J. 2025. PMID: 38734409 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combining Nanopore direct RNA sequencing with genetics and mass spectrometry for analysis of T-loop base modifications across 42 yeast tRNA isoacceptors.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Oct 28;52(19):12074-12092. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae796. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 39340295 Free PMC article.
-
Past, Present, and Future of RNA Modifications in Infectious Disease Research.ACS Infect Dis. 2024 Dec 13;10(12):4017-4029. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.4c00598. Epub 2024 Nov 21. ACS Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 39569943
References
-
- World malaria report. WHOhttps://www.mmv.org/sites/default/files/content/document/world-malaria-r... (2023).
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

