miR-124-3p and miR-194-5p regulation of the PI3K/AKT pathway via ROR2 in medulloblastoma progression
- PMID: 38632356
- PMCID: PMC11192632
- DOI: 10.1038/s41417-024-00762-y
miR-124-3p and miR-194-5p regulation of the PI3K/AKT pathway via ROR2 in medulloblastoma progression
Abstract
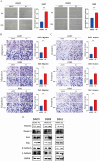
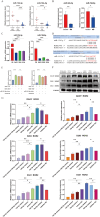
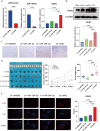
Medulloblastoma (MB), a prevalent pediatric central nervous system tumor, is influenced by microRNAs (miRNAs) that impact tumor initiation and progression. However, the specific involvement of miRNAs in MB tumorigenesis remains unclear. Using single-cell RNA sequencing, we identified ROR2 expression in normal human fetal cerebellum. Subsequent analyses, including immunofluorescence, quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR), and Western blot, assessed ROR2 expression in MB tissues and cell lines. We investigated miR-124-3p and miR-194-5p and their regulatory role in ROR2 expression through the dual-luciferase reporter, qRT-PCR, and western blot assays. Mechanistic insights were gained through functional assays exploring the impact of miR-124-3p, miR-194-5p, and ROR2 on MB growth in vitro and in vivo. We observed significantly reduced miR-124-3p and miR-194-5p expression and elevated ROR2 expression in MB tissues and cell lines. High ROR2 expression inversely correlated with overall survival in WNT and SHH subgroups of MB patients. Functionally, overexpressing miR-124-3p and miR-194-5p and inhibiting ROR2 suppressed in vitro malignant transformation and in vivo tumorigenicity. Mechanistically, miR-124-3p and miR-194-5p synergistically regulated the ROR2/PI3K/Akt pathway, influencing MB progression. Our findings indicate that miR-124-3p and miR-194-5p function as tumor suppressors, inhibiting MB progression via the ROR2/PI3K/Akt axis, suggesting a key mechanism and therapeutic targets for MB patients.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Circ_0044520 regulates the progression of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma via the miR-338-3p/ROR2 axis.Histol Histopathol. 2022 Jun;37(6):513-526. doi: 10.14670/HH-18-420. Epub 2022 Jan 17. Histol Histopathol. 2022. PMID: 35037694
-
Long Noncoding RNA TUG1 Promotes the Function in ox-LDL-Treated HA-VSMCs via miR-141-3p/ROR2 Axis.Cardiovasc Ther. 2020 May 29;2020:6758934. doi: 10.1155/2020/6758934. eCollection 2020. Cardiovasc Ther. 2020. PMID: 32565910 Free PMC article.
-
A-to-I-Edited miR-1304-3p Inhibits Glycolysis and Tumor Growth of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma by Inactivating Wnt5a/ROR2 Signaling.Mol Carcinog. 2025 Mar;64(3):552-564. doi: 10.1002/mc.23867. Epub 2025 Jan 6. Mol Carcinog. 2025. PMID: 39763297 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the role of miR-767 in tumor progression: Mechanisms and clinical implications.Gene. 2025 May 15;949:149366. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2025.149366. Epub 2025 Feb 27. Gene. 2025. PMID: 40023339 Review.
-
The intersections between neuroscience and medulloblastoma.Cancer Lett. 2025 Jun 28;620:217660. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2025.217660. Epub 2025 Mar 26. Cancer Lett. 2025. PMID: 40154912 Review.
Cited by
-
EZH2: A Crucial Competing Endogenous RNA in Cancer Research-A Scoping Review.Adv Biomed Res. 2025 May 31;14:53. doi: 10.4103/abr.abr_561_24. eCollection 2025. Adv Biomed Res. 2025. PMID: 40519579 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of PI3K Levels and miRNA124-5p Expression Levels in Serum Samples from Patients With Lung Cancer.Cancer Diagn Progn. 2025 Mar 3;5(2):223-229. doi: 10.21873/cdp.10433. eCollection 2025 Mar-Apr. Cancer Diagn Progn. 2025. PMID: 40034961 Free PMC article.
-
The dual role of circHIPK3 in cancer and its implications for multiple drugs resistance: a systematic review and computational approach.Front Oncol. 2025 Feb 21;15:1547889. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1547889. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40061896 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Role of hsa_circ_0052112 as a Potential Biomarker in Breast Cancer: Insights from Experimental and In Silico Analyses.Avicenna J Med Biotechnol. 2025 Apr-Jun;17(2):136-146. doi: 10.18502/ajmb.v17i2.18565. Avicenna J Med Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40453910 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jakacki RI, Burger PC, Zhou T, Holmes EJ, Kocak M, Onar A, et al. Outcome of children with metastatic medulloblastoma treated with carboplatin during craniospinal radiotherapy: a Children’s Oncology Group Phase I/II study. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30:2648–53. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2011.40.2792. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

