Vimentin filaments integrate low-complexity domains in a complex helical structure
- PMID: 38632361
- PMCID: PMC11189308
- DOI: 10.1038/s41594-024-01261-2
Vimentin filaments integrate low-complexity domains in a complex helical structure
Abstract
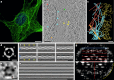
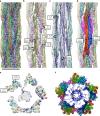
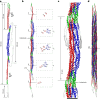
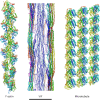
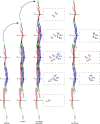
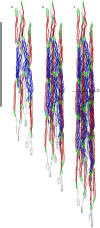
Intermediate filaments (IFs) are integral components of the cytoskeleton. They provide cells with tissue-specific mechanical properties and are involved in numerous cellular processes. Due to their intricate architecture, a 3D structure of IFs has remained elusive. Here we use cryo-focused ion-beam milling, cryo-electron microscopy and tomography to obtain a 3D structure of vimentin IFs (VIFs). VIFs assemble into a modular, intertwined and flexible helical structure of 40 α-helices in cross-section, organized into five protofibrils. Surprisingly, the intrinsically disordered head domains form a fiber in the lumen of VIFs, while the intrinsically disordered tails form lateral connections between the protofibrils. Our findings demonstrate how protein domains of low sequence complexity can complement well-folded protein domains to construct a biopolymer with striking mechanical strength and stretchability.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


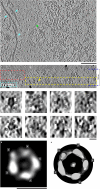
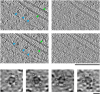

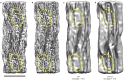


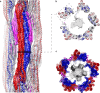
Similar articles
-
Are the Head and Tail Domains of Intermediate Filaments Really Unstructured Regions?Genes (Basel). 2024 May 16;15(5):633. doi: 10.3390/genes15050633. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38790262 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural analysis of vimentin and keratin intermediate filaments by cryo-electron tomography.Exp Cell Res. 2007 Jun 10;313(10):2217-27. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2007.03.037. Epub 2007 Apr 11. Exp Cell Res. 2007. PMID: 17499715 Review.
-
Three-dimensional cryo-electron microscopy on intermediate filaments.Methods Cell Biol. 2010;96:565-89. doi: 10.1016/S0091-679X(10)96023-8. Methods Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20869538
-
Dissecting the 3-D structure of vimentin intermediate filaments by cryo-electron tomography.J Struct Biol. 2007 Jun;158(3):378-85. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2006.12.007. Epub 2006 Dec 28. J Struct Biol. 2007. PMID: 17289402
-
Towards a molecular description of intermediate filament structure and assembly.Exp Cell Res. 2007 Jun 10;313(10):2204-16. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2007.04.009. Epub 2007 Apr 12. Exp Cell Res. 2007. PMID: 17521629 Review.
Cited by
-
Are the Head and Tail Domains of Intermediate Filaments Really Unstructured Regions?Genes (Basel). 2024 May 16;15(5):633. doi: 10.3390/genes15050633. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38790262 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Practical Guide for Implementing Cryogenic Electron Microscopy Structure Determination in Dermatology Research.J Invest Dermatol. 2025 Jan;145(1):22-31. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2024.10.594. Epub 2024 Nov 26. J Invest Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 39601740 Review.
-
Vimentin undergoes liquid-liquid phase separation to form droplets which wet and stabilize actin fibers.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 Mar 11;122(10):e2418624122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2418624122. Epub 2025 Mar 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025. PMID: 40030010
-
Unveiling the secrets of vimentin filament architecture relevant to human disease.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2024 Jun;31(6):849-851. doi: 10.1038/s41594-024-01301-x. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38684931 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Reconstitution of lamin assembly on nuclear pore complex-containing membranes.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jul 30:2025.07.28.667287. doi: 10.1101/2025.07.28.667287. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40766420 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

