Genetic barriers more than environmental associations explain Serratia marcescens population structure
- PMID: 38632370
- PMCID: PMC11023947
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-024-06069-w
Genetic barriers more than environmental associations explain Serratia marcescens population structure
Abstract
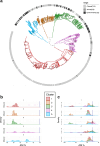
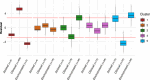
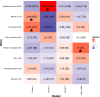
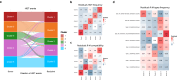
Bacterial species often comprise well-separated lineages, likely emerged and maintained by genetic isolation and/or ecological divergence. How these two evolutionary actors interact in the shaping of bacterial population structure is currently not fully understood. In this study, we investigate the genetic and ecological drivers underlying the evolution of Serratia marcescens, an opportunistic pathogen with high genomic flexibility and able to colonise diverse environments. Comparative genomic analyses reveal a population structure composed of five deeply-demarcated genetic clusters with open pan-genome but limited inter-cluster gene flow, partially explained by Restriction-Modification (R-M) systems incompatibility. Furthermore, a large-scale research on hundred-thousands metagenomic datasets reveals only a partial habitat separation of the clusters. Globally, two clusters only show a separate gene composition coherent with ecological adaptations. These results suggest that genetic isolation has preceded ecological adaptations in the shaping of the species diversity, an evolutionary scenario coherent with the Evolutionary Extended Synthesis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Global population structure of the Serratia marcescens complex and identification of hospital-adapted lineages in the complex.Microb Genom. 2022 Mar;8(3):000793. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.000793. Microb Genom. 2022. PMID: 35315751 Free PMC article.
-
Genome evolution and plasticity of Serratia marcescens, an important multidrug-resistant nosocomial pathogen.Genome Biol Evol. 2014 Aug;6(8):2096-110. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evu160. Genome Biol Evol. 2014. PMID: 25070509 Free PMC article.
-
Distribution and Genetic Diversity of Genes Involved in Quorum Sensing and Prodigiosin Biosynthesis in the Complete Genome Sequences of Serratia marcescens.Genome Biol Evol. 2019 Mar 1;11(3):931-936. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evz046. Genome Biol Evol. 2019. PMID: 30840067 Free PMC article.
-
[Efflux systems in Serratia marcescens].Mikrobiologiia. 2014 Jan-Feb;83(1):3-14. Mikrobiologiia. 2014. PMID: 25423729 Review. Russian.
-
Serratia marcescens antibiotic resistance mechanisms of an opportunistic pathogen: a literature review.PeerJ. 2023 Jan 5;11:e14399. doi: 10.7717/peerj.14399. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 36627920 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cultivation and sequencing-free protocol for Serratia marcescens detection and typing.iScience. 2024 Mar 1;27(4):109402. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109402. eCollection 2024 Apr 19. iScience. 2024. PMID: 38510115 Free PMC article.

