The dual role of Spn-E in supporting heterotypic ping-pong piRNA amplification in silkworms
- PMID: 38632376
- PMCID: PMC11094040
- DOI: 10.1038/s44319-024-00137-2
The dual role of Spn-E in supporting heterotypic ping-pong piRNA amplification in silkworms
Abstract
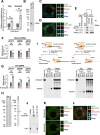
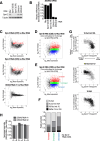
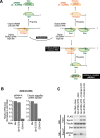
The PIWI-interacting RNA (piRNA) pathway plays a crucial role in silencing transposons in the germline. piRNA-guided target cleavage by PIWI proteins triggers the biogenesis of new piRNAs from the cleaved RNA fragments. This process, known as the ping-pong cycle, is mediated by the two PIWI proteins, Siwi and BmAgo3, in silkworms. However, the detailed molecular mechanism of the ping-pong cycle remains largely unclear. Here, we show that Spindle-E (Spn-E), a putative ATP-dependent RNA helicase, is essential for BmAgo3-dependent production of Siwi-bound piRNAs in the ping-pong cycle and that this function of Spn-E requires its ATPase activity. Moreover, Spn-E acts to suppress homotypic Siwi-Siwi ping-pong, but this function of Spn-E is independent of its ATPase activity. These results highlight the dual role of Spn-E in facilitating proper heterotypic ping-pong in silkworms.
Keywords: BmAgo3; Ping-Pong Cycle; Siwi; Spn-E; piRNA.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

